Image-guided percutaneous splenic biopsy and drainage
- PMID: 24293803
- PMCID: PMC3577624
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1330064
Image-guided percutaneous splenic biopsy and drainage
Abstract
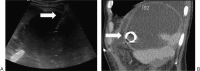
Percutaneous splenic biopsy and drainage are relatively safe and accurate procedures. The risk of major complication (1.3%) following percutaneous splenic biopsy does not exceed that of other solid intra-abdominal organ biopsies, and it has less morbidity and mortality than splenectomy. Both computed tomography and ultrasound can be used to provide image guidance for biopsy and drainage. The safety profile of fine-needle aspiration cytology is better than core needle biopsy, but core biopsy has superior diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: biopsy; computed tomography; drainage; interventional radiology; spleen; ultrasound.
Figures
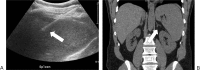
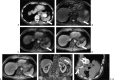
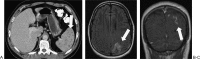
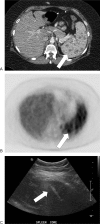
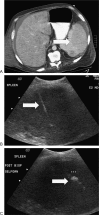
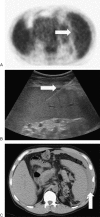
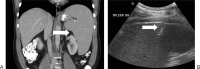
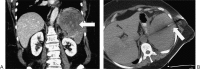
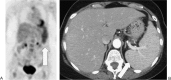
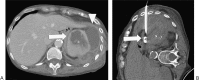
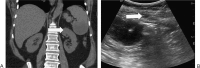
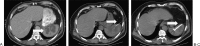
References
-
- Bhatia K, Sahdev A, Reznek R H. Lymphoma of the spleen. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2007;28(1):12–20. - PubMed
-
- Kamaya A, Weinstein S, Desser T S. Multiple lesions of the spleen: differential diagnosis of cystic and solid lesions. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2006;27(5):389–403. - PubMed
-
- McInnes M D, Kielar A Z, Macdonald D B. Percutaneous image-guided biopsy of the spleen: systematic review and meta-analysis of the complication rate and diagnostic accuracy. Radiology. 2011;260(3):699–708. - PubMed
-
- Tam A, Krishnamurthy S, Pillsbury E P. et al.Percutaneous image-guided splenic biopsy in the oncology patient: an audit of 156 consecutive cases. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008;19(1):80–87. - PubMed
-
- Lucey B C, Boland G W, Maher M M, Hahn P F, Gervais D A, Mueller P R. Percutaneous nonvascular splenic intervention: a 10-year review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179(6):1591–1596. - PubMed

