Corticocancellous olecranon autograft for metacarpal defect reconstruction: a case report
- PMID: 24294172
- PMCID: PMC3508013
- DOI: 10.1007/s11552-012-9444-y
Corticocancellous olecranon autograft for metacarpal defect reconstruction: a case report
Abstract
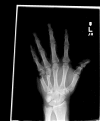
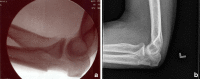
Background: High-energy injuries to the hand frequently lead to bone defects as well as soft tissue loss. Early bone grafting of defects is well established in the literature; however, few options are available for autologous corticocancellous grafts. Most frequently cited studies describe the iliac crest or the distal radius donor sites.
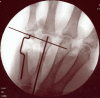
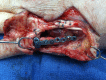
Methods: In this case report, we describe a new technique of obtaining corticocancellous bone graft from the olecranon.
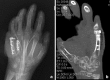
Results: Complete union of the segmental defect was achieved with this technique.
Conclusions: The olecranon donor site is outside the zone of injury and therefore safe to access, but within the upper extremity, thus avoiding the need for harvest from a distant site such as the iliac crest or the distal femur. Additional benefits of this site are the greater volume of graft that can be harvested compared to the distal radius as well as a more optimal ratio of cancellous to cortical graft available, compared to the iliac crest where the graft may be excessively cortical in nature.
Keywords: Autograft; Bone defect; Metacarpal; Olecranon.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bone graft harvesting from the distal radius, olecranon, and iliac crest: a quantitative analysis.J Hand Surg Am. 2001 Jan;26(1):135-41. doi: 10.1053/jhsu.2001.20971. J Hand Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11172380
-
Thumb proximal phalanx reconstruction with nonvascularized corticocancellous olecranon bone graft.Orthopedics. 2015 Jan;38(1):58-61. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20150105-90. Orthopedics. 2015. PMID: 25611412
-
[Minimally Invasive Cancellous Bone Graft Harvesting in Trauma Indication - Clinical Part of the Study].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2020;87(2):108-113. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2020. PMID: 32396511 Czech.
-
Incidence of donor site morbidity following harvesting from iliac crest or RIA graft.Injury. 2014 Dec;45 Suppl 6:S116-20. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2014.10.034. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Injury. 2014. PMID: 25457330 Review.
-
Autogenous bone graft: donor sites and techniques.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011 Dec 7;93(23):2227-36. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.01513. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011. PMID: 22159859 Review.
Cited by
-
Reconstruction of a Complex Metacarpal Shaft Fracture With Segmental Bone Loss Using Autologous Iliac Crest Bone Graft.Eplasty. 2015 Aug 20;15:ic47. eCollection 2015. Eplasty. 2015. PMID: 26336573 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparing Morbidities of Bone Graft Harvesting from the Olecranon Process and the Distal Radius.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016 Feb 19;4(2):e623. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000617. eCollection 2016 Feb. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016. PMID: 27014552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruner J. Use of single iliac-bone graft to replace multiple metacarpal loss is dorsal injuries of the hand. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957;39:43–52. - PubMed
-
- Bruno RJ, Cohen MS, Berzins A, et al. Bone graft harvesting from the distal radius, olecranon, and iliac crest: a quantitative analysis. J Hand Surg. 2001;26A:135–141. - PubMed
-
- Calkins MS, Burkhalter W, Reyes F. Traumatic segmental bone defects in the upper extremity. J Bone Joint Surg. 1987;69(A):19–27. - PubMed
-
- Freeland AE, Jabaley ME. Stabilization of fractures in the hand and wrist with traumatic soft tissue and bone loss. Hand Clin. 1988;4:425–436. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

