Comparing the expression of integrins αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ6, αvβ8, fibronectin and fibrinogen in human brain metastases and their corresponding primary tumors
- PMID: 24294359
- PMCID: PMC3843253
Comparing the expression of integrins αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ6, αvβ8, fibronectin and fibrinogen in human brain metastases and their corresponding primary tumors
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the expression of αv-series integrins in brain metastases. Inhibitors targeting these integrins are being tested for their therapeutic potential.
Material and method: The extracellular regions of the αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ6, αvβ8, the cytoplasmic domain of β3, the αv-chain, and the ECM molecules fibronectin and fibrinogen were studied immunohistochemically in a series of 122 carcinoma and 60 melanomas metastatic to the central nervous system. In addition, 38 matched primary and metastatic tumors to the brain were compared directly.
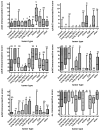
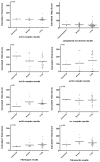
Results: The αv-subunit was generally moderately to highly expressed in most tumors. αvβ3 and cytoplasmic β3 were weakly to moderately detectable in metastatic renal cell carcinomas and melanomas, αvβ5 was prominently expressed in metastatic renal and colorectal carcinomas, αvβ6 was most abundantly detectable in metastatic lung adenocarcinomas, but absent in melanomas. The tumor associated vessels in CNS metastases consistently expressed αvβ3, αvβ5, αv-, fibronectin and fibrinogen, however, mostly at low levels, while αvβ6, αvβ8 were lacking in vasculature. The comparative analysis of 38 matched primary tumors and brain metastases showed comparable levels of expression only for αvβ3 and αvβ8, while αvβ6 and αvβ5 were higher in primaries.
Conclusion: We confirmed that integrin expression exhibits considerable heterogeneity according to tumor origin. αvβ5 is the most promising target for integrin targeted treatment in brain metastases.
Keywords: Integrins; alphav; metastases; prognosis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
αv-Integrin isoform expression in primary human tumors and brain metastases.Int J Cancer. 2013 Nov 15;133(10):2362-71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28267. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23661241
-
Expression of integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 and their ligands in primary and secondary central nervous system neoplasms.Histol Histopathol. 2013 Jun;28(6):749-58. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.749. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Histol Histopathol. 2013. PMID: 23238957
-
αvβ3, αvβ5 and αvβ6 integrins in brain metastases of lung cancer.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2014 Oct;31(7):841-51. doi: 10.1007/s10585-014-9675-0. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2014. PMID: 25150423
-
alphaV Integrins on HT-29 colon carcinoma cells: adhesion to fibronectin is mediated solely by small amounts of alphaVbeta6, and alphaVbeta5 is codistributed with actin fibers.Exp Cell Res. 1997 Jul 10;234(1):156-64. doi: 10.1006/excr.1997.3599. Exp Cell Res. 1997. PMID: 9223381
-
RGD-Binding Integrins in Head and Neck Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2017 May 26;9(6):56. doi: 10.3390/cancers9060056. Cancers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28587135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer cells remodel themselves and vasculature to overcome the endothelial barrier.Cancer Lett. 2016 Oct 1;380(2):534-544. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.031. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 25449784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Predictive Link between Matrix and Metastasis.Curr Opin Chem Eng. 2016 Feb;11:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2016.01.001. Curr Opin Chem Eng. 2016. PMID: 26942108 Free PMC article.
-
Phoyunnanin E inhibits migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells via suppression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and integrin αv and integrin β3.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Dec 29;17(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-2059-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 29284478 Free PMC article.
-
Cilengitide, an αvβ3-integrin inhibitor, enhances the efficacy of anti-programmed cell death-1 therapy in a murine melanoma model.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):4557-4572. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2029236. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35142593 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis-inducing proteins are widely expressed in human brain metastases and associated with intracranial progression and radiation response.Br J Cancer. 2016 May 10;114(10):1101-8. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.103. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27100728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Lillehei KO, Breeze RE. Neoplasms involving the central nervous system in the older old. Hum Pathol. 2003;34:1137–1147. - PubMed
-
- Gavrilovic IT, Posner JB. Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol. 2005;75:5–14. - PubMed
-
- Ray S, Dacosta-Byfield S, Ganguli A, Bonthapally V, Teitelbaum A. Comparative analysis of survival, treatment, cost and resource use among patients newly diagnosed with brain metastasis by initial primary cancer. J Neurooncol. 2013;114:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;37:745–51. - PubMed
-
- Preusser M, Capper D, Ilhan-Mutlu A, Berghoff AS, Birner P, Bartsch R, Marosi C, Zielinski C, Mehta MP, Winkler F, Wick W, von Deimling A. Brain metastases: pathobiology and emerging targeted therapies. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;123:205–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
