KAT5 and KAT6B are in positive regulation on cell proliferation of prostate cancer through PI3K-AKT signaling
- PMID: 24294372
- PMCID: PMC3843266
KAT5 and KAT6B are in positive regulation on cell proliferation of prostate cancer through PI3K-AKT signaling
Abstract
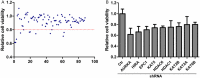
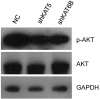
Histone modifications play important roles in the tumorigenesis and progression of prostate cancer (PCa) and genes involved in histone modifications are seemed as ideal targets for treatment of PCa patients. However, clinical trials have shown that those existing drugs exert the minimal antitumor activity and excess adverse effects on PCa patients. Therefore, it is of great interest to figure out novel specific biomarkers to guide the development of new drugs. In present study, an RNAi screening with 44 genes involved in histone modifications was applied to a PCa cell line, Du145. The results showed that nine genes were in positive regulation of Du145 cell growth. Then four selected genes (KAT2B, KAT5, KAT6B and HDAC1) were found to exert this effect by a gene-specific manner when silenced. And then KAT5 or KAT6B silenced cells were subjected to DNA microarray analysis. The common differentially expressed genes were analyzed by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) and found that PDEF signaling, EIF2 signaling and PI3K signaling was suppressed following by KAT5 or KAT6B silencing. Subsequent immunoblotting assay showed that AKT signaling was inhibited, which suggested that KAT5 or KAT6B regulates cancer cell growth through PI3K-AKT signaling. Together with our published data [31] that AURKA inhibitoin increased drug sensitivity of DU145, our work demonstrated the underlying mechanism that how the acetylation enzyme regulates cancer cells survial and might provide potential therapeutic targets for prostate cancer patients in future epigenetic drug development.
Keywords: KAT5; KAT6B; PI3K-AKT signaling; Prostate cancer; RNAi screening; histone modifications.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 72 homolog (VPS72) binding to lysine acetyltransferase 5 (KAT5) promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):9197-9210. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2056692. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35383533 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT3 inhibits prostate cancer by destabilizing oncoprotein c-MYC through regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 22;6(28):26494-507. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4764. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26317998 Free PMC article.
-
KAT5 silencing induces apoptosis of GBC-SD cells through p38MAPK-mediated upregulation of cleaved Casp9.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 Dec 15;7(1):80-91. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24427328 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K/AKT pathway in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016 Jun 1;21(5):1084-91. doi: 10.2741/4443. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016. PMID: 27100493 Review.
-
The key roles of the lysine acetyltransferases KAT6A and KAT6B in physiology and pathology.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100729. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100729. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33130515 Review.
Cited by
-
KAT5 Negatively regulates the proliferation of prostate cancer LNCaP cells via the caspase 3-dependent apoptosis pathway.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2019 Aug 1;23(4):253-259. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2019.1644372. eCollection 2019. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2019. PMID: 31489246 Free PMC article.
-
Target Identification Using Homopharma and Network-Based Methods for Predicting Compounds Against Dengue Virus-Infected Cells.Molecules. 2020 Apr 18;25(8):1883. doi: 10.3390/molecules25081883. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32325755 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Acetyltransferase KAT6A Upregulates PI3K/AKT Signaling through TRIM24 Binding.Cancer Res. 2017 Nov 15;77(22):6190-6201. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1388. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29021135 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Histone Acetyltransferases and Histone Deacetylases on Adult Brain Myelin Plasticity.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2025;75:213-246. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-91459-1_8. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2025. PMID: 40593212 Review.
-
Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 72 homolog (VPS72) binding to lysine acetyltransferase 5 (KAT5) promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):9197-9210. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2056692. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35383533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin. 2003;53:5–26. - PubMed
-
- Schuster-Bockler B, Lehner B. Chromatin organization is a major influence on regional mutation rates in human cancer cells. Nature. 2012;488:504–507. - PubMed
-
- Perry AS, Watson RW, Lawler M, Hollywood D. The epigenome as a therapeutic target in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2010;7:668–680. - PubMed
-
- Korkmaz CG, Fronsdal K, Zhang Y, Lorenzo PI, Saatcioglu F. Potentiation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity by inhibition of histone deacetylation--rescue of transcriptionally compromised mutants. J Endocrinol. 2004;182:377–389. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
