Post cardiac transplantation T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder presenting as a solitary lung nodule
- PMID: 24294392
- PMCID: PMC3843286
Post cardiac transplantation T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder presenting as a solitary lung nodule
Abstract
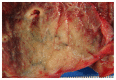
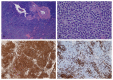
Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is an infrequent, but serious complication of solid organ and bone marrow transplantations. The vast majority of the cases are of B-cell origin and usually associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. The non-B (T and NK cell) PTLDs account for up to 14% of the PTLD cases in Western countries. We report a case of a 66-year-old man who received an orthotopic heart transplant for cardiomyopathy 7 years prior to presentation. He was referred to our institution with a hypermetabolic solitary right lower lobe lung nodule with an SUV of 9.2 on PET scan. The combined histomorphological and immunohistochemical pattern was most consistent with monomorphic PTLD, peripheral T-cell lymphoma with angioimmunoblastic features. Molecular studies showed clonal T-cell gamma receptor gene rearrangement. Primary pulmonary involvement of T-cell PTLD is extremely rare. This is the third reported case of T-cell PTLD after cardiac transplantation, primarily involving the lung. Further, studies will be required to determine the appropriate treatment and prognosis of this rare entity.
Keywords: PTLD; T-cell lymphoma; heart transplantation; lung nodule.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T gamma/delta hepatosplenic lymphoma in a heart transplant patient after an Epstein-Barr virus positive lymphoproliferative disorder: a case report.Cancer. 1998 Mar 1;82(5):983-92. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19980301)82:5<983::aid-cncr26>3.0.co;2-w. Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9486591
-
T-cell lymphoma with a granulomatous lesion of the lungs after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a unique rare case of metachronous B-cell and T-cell lymphoma.Diagn Pathol. 2020 Oct 9;15(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13000-020-01038-3. Diagn Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33036636 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma associated with Epstein-Barr virus following cardiac transplant.Am J Surg Pathol. 2004 Mar;28(3):410-5. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200403000-00018. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15104308
-
T-cell posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder occurring in a pediatric solid-organ transplant patient.Am J Surg Pathol. 2004 Jul;28(7):967-73. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200407000-00019. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15223970 Review.
-
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: T-cell lymphoma following cardiac transplant.Leuk Lymphoma. 2002 Feb;43(2):447-50. doi: 10.1080/10428190290006332. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002. PMID: 11999587 Review.
References
-
- Mihalov ML, Gattuso P, Abraham K, Holmes EW, Reddy V. Incidence of post-transplant malignancy among 674 solid-organ-transplant recipients at a single center. Clin Transplant. 1996;10:248. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Pileri S, Stein H, Jaffe ES. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC; 2008.
-
- Wasson S, Zafar MN, Best J, Reddy HK. Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder in heart and kidney transplant patients: a single-center experience. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2006;11:77–83. - PubMed
-
- Ghobrial IM, Habermann TM, Maurer MJ, Geyer SM, Ristow KM, Larson TS, Walker RC, Ansell SM, Macon WR, Gores GG, Stegall MD, McGregor CG. Prognostic analysis for survival in adult solid organ transplant recipients with post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7574–82. - PubMed
-
- Allen U, Hebert D, Moore D, Dror Y, Wasfy S. Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease in solid organ transplant recipients, 1988-97: a Canadian multi-centre experience. Pediatr Transplant. 2001;5:198–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
