Characteristics and management of superior semicircular canal dehiscence
- PMID: 24294552
- PMCID: PMC3578588
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1324397
Characteristics and management of superior semicircular canal dehiscence
Abstract
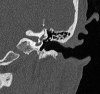
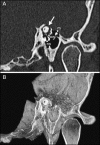
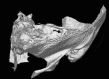
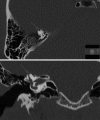
Objectives To review the characteristic symptoms of superior semicircular canal dehiscence, testing and imaging of the disease, and the current treatment and surgical options. Results and Conclusions Symptoms of superior semicircular canal dehiscence (SSCD) include autophony, inner ear conductive hearing loss, Hennebert sign, and sound-induced episodic vertigo and disequilibrium (Tullio phenomenon), among others. Potential etiologies noted for canal dehiscence include possible developmental abnormalities, congenital defects, chronic otitis media with cholesteatoma, fibrous dysplasia, and high-riding jugular bulb. Computed tomography (CT), vestibular evoked myogenic potentials, Valsalva maneuvers, and certain auditory testing may prove useful in the detection and evaluation of dehiscence syndrome. Multislice temporal bone CT examinations are normally performed with fine-cut (0.5- to 0.6-mm) collimation reformatted to the plane of the superior canal such that images are parallel and orthogonal to the plane. For the successful alleviation of auditory and vestibular symptoms, a bony dehiscence can be surgically resurfaced, plugged, or capped through a middle fossa craniotomy or the transmastoid approach. SSCD should only be surgically treated in patients who exhibit clinical manifestations.
Keywords: Tullio phenomenon; autophony; hearing loss; superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome; vertigo.
Figures
References
-
- Chien W W, Carey J P, Minor L B. Canal dehiscence. Curr Opin Neurol. 2011;24:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Amoodi H A, Makki F M, McNeil M, Bance M. Transmastoid resurfacing of superior semicircular canal dehiscence. Laryngoscope. 2011;121:1117–1123. - PubMed
-
- Minor L B. Clinical manifestations of superior semicircular canal dehiscence. Laryngoscope. 2005;115:1717–1727. - PubMed
-
- Friedland D R, Michel M A. Cranial thickness in superior canal dehiscence syndrome: implications for canal resurfacing surgery. Otol Neurotol. 2006;27:346–354. - PubMed
-
- Minor L B, Carey J P, Cremer P D, Lustig L R, Streubel S O, Ruckenstein M J. Dehiscence of bone overlying the superior canal as a cause of apparent conductive hearing loss. Otol Neurotol. 2003;24:270–278. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

