Similar-case-based optimization of beam arrangements in stereotactic body radiotherapy for assisting treatment planners
- PMID: 24294603
- PMCID: PMC3835834
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/309534
Similar-case-based optimization of beam arrangements in stereotactic body radiotherapy for assisting treatment planners
Abstract
Objective: To develop a similar-case-based optimization method for beam arrangements in lung stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) to assist treatment planners.
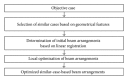
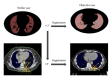
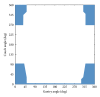
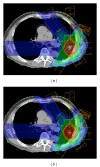
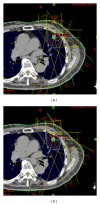
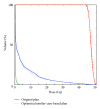
Methods: First, cases that are similar to an objective case were automatically selected based on geometrical features related to a planning target volume (PTV) location, PTV shape, lung size, and spinal cord position. Second, initial beam arrangements were determined by registration of similar cases with the objective case using a linear registration technique. Finally, beam directions of the objective case were locally optimized based on the cost function, which takes into account the radiation absorption in normal tissues and organs at risk. The proposed method was evaluated with 10 test cases and a treatment planning database including 81 cases, by using 11 planning evaluation indices such as tumor control probability and normal tissue complication probability (NTCP).
Results: The procedure for the local optimization of beam arrangements improved the quality of treatment plans with significant differences (P < 0.05) in the homogeneity index and conformity index for the PTV, V10, V20, mean dose, and NTCP for the lung.
Conclusion: The proposed method could be usable as a computer-aided treatment planning tool for the determination of beam arrangements in SBRT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computer-aided beam arrangement based on similar cases in radiation treatment-planning databases for stereotactic lung radiation therapy.J Radiat Res. 2013 May;54(3):569-77. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrs123. Epub 2012 Dec 18. J Radiat Res. 2013. PMID: 23249674 Free PMC article.
-
TU-E-BRB-01: Similar-Case-Based Optimization of Beam Arrangements in Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy.Med Phys. 2012 Jun;39(6Part24):3908. doi: 10.1118/1.4735950. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 28518700
-
Similar-cases-based planning approaches with beam angle optimizations using water equivalent path length for lung stereotactic body radiation therapy.Radiol Phys Technol. 2020 Jun;13(2):119-127. doi: 10.1007/s12194-020-00558-3. Epub 2020 Mar 14. Radiol Phys Technol. 2020. PMID: 32172525
-
Circumferential or sectored beam arrangements for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) of primary lung tumors: effect on target and normal-structure dose-volume metrics.Med Dosim. 2013 Winter;38(4):407-12. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Med Dosim. 2013. PMID: 23810414
-
Assessment of Monte Carlo algorithm for compliance with RTOG 0915 dosimetric criteria in peripheral lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 May 8;17(3):277-293. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i3.6077. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27167284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagata Y, Wulf J, Lax I, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy of primary lung cancer and other targets: results of consultant meeting of the international atomic energy agency. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2011;79(3):660–669. - PubMed
-
- Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable Stage i non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery? International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2011;81(5):1352–1358. - PubMed
-
- Taremi M, Hope A, Dahele M, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for medically inoperable lung cancer: prospective, single-center study of 108 consecutive patients. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2012;82(2):967–973. - PubMed
-
- Takayama K, Nagata Y, Negoro Y, et al. Treatment planning of stereotactic radiotherapy for solitary lung tumor. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2005;61(5):1565–1571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

