Cellular biochemistry methods for investigating protein tyrosine phosphatases
- PMID: 24294920
- PMCID: PMC3995294
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5731
Cellular biochemistry methods for investigating protein tyrosine phosphatases
Abstract
Significance: The protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) are a family of proteins that play critical roles in cellular signaling and influence many aspects of human health and disease. Although a wealth of information has been collected about PTPs since their discovery, many questions regarding their regulation and function still remain.
Critical issues: Of particular importance are the elucidation of the biological substrates of individual PTPs and understanding of the chemical and biological basis for temporal and spatial resolution of PTP activity within a cell.
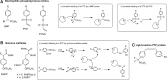
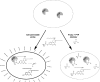
Recent advances: Drawing from recent advances in both biology and chemistry, innovative approaches have been developed to study the intracellular biochemistry and physiology of PTPs. We provide a summary of PTP-tailored techniques and approaches, emphasizing methodologies to study PTP activity within a cellular context. We first provide a discussion of methods for identifying PTP substrates, including substrate-trapping mutants and synthetic peptide libraries for substrate selectivity profiling. We next provide an overview of approaches for monitoring intracellular PTP activity, including a discussion of mechanistic-based probes, gel-based assays, substrates that can be used intracellularly, and assays tied to cell growth. Finally, we review approaches used for monitoring PTP oxidation, a key regulatory pathway for these enzymes, discussing the biotin switch method and variants of this approach, along with affinity trapping techniques and probes designed to detect PTP oxidation.
Future directions: Further development of approaches to investigate the intracellular PTP activity and functions will provide specific insight into their mechanisms of action and control of diverse signaling pathways.
Figures






References
-
- Agazie YM. and Hayman MJ. Development of an efficient “substrate-trapping” mutant of Src homology phosphotyrosine phosphatase 2 and identification of the epidermal growth factor receptor, Gab1, and three other proteins as target substrates. J Biol Chem 278: 13952–13958, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Alonso A, Sasin J, Bottini N, Friedberg I, Friedberg I, Osterman A, et al. . Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 117: 699–711, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Baba H, Masuda Y, Sueyoshi N, and Kameshita I. In-gel phosphatase assay using non-denaturing two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Biochem 152: 557–563, 2012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

