Functional single nucleotide polymorphisms of the RASSF3 gene and susceptibility to squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- PMID: 24295637
- PMCID: PMC3946894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.11.009
Functional single nucleotide polymorphisms of the RASSF3 gene and susceptibility to squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
Abstract
Background: RASSF3 suppresses tumour formation through uncertain mechanisms, but it is an important gene of p53-dependent apoptosis. RASSF3 depletion impairs DNA repair after DNA damage, leading to polyploidy. The authors hypothesised that potential functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of RASSF3 are associated with risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN).
Methods: The authors used a functional SNP approach to evaluate the associations between common (minor allele frequency⩾0.05), putative functional variants in RASSF3 and risk of SCCHN. Four selected such functional SNPs (rs6581580 T>G, rs7313765 G>A, rs12311754 G>C and rs1147098 T>C) in RASSF3 were identified and genotyped in 1087 patients and 1090 cancer-free controls in a non-Hispanic white population.
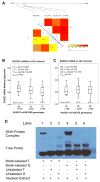
Results: The authors found that two SNPs were significantly associated with SCCHN risk. Carriers of the variant rs6581580G and rs7313765A alleles were at a reduced SCCHN risk, compared with the corresponding common homozygotes [adjusted odds ratio (OR)=0.75 and 0.73 and 95% confidence interval (CI)=0.62-0.91 and 0.60-0.88, respectively, for dominant models; and Ptrend=0.012 and 0.041, respectively, for additive models], particularly for non-oropharyngeal tumours (adjusted OR=0.68 and 0.60 and 95% CI=0.53-0.86 and 0.47-0.77, respectively, for dominant models). In the genotype-phenotype correlation analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 102 cancer-free controls, the rs6581580 GG genotype was associated with significantly increased expression levels of RASSF3 mRNA (P=0.038), compared with the TT genotype. Additional functional experiments further showed that variant G allele of rs6581580 had a significantly stronger binding affinity to the nuclear protein extracts than the T allele.
Conclusion: Taken together, these findings indicate that the RASSF3 promoter rs6581580 T>G SNP is potentially functional, modulating susceptibility to SCCHN among non-Hispanic whites. Larger replication studies are needed to confirm our findings.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Biomarker; Genetic susceptibility; Head and neck cancer; Polymorphism; RASSF3.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A functional variant at the miR-885-5p binding site of CASP3 confers risk of both index and second primary malignancies in patients with head and neck cancer.FASEB J. 2013 Apr;27(4):1404-12. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-223420. Epub 2012 Dec 27. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23271051 Free PMC article.
-
A functional variant at the miR-184 binding site in TNFAIP2 and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Nov;32(11):1668-74. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr209. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21934093 Free PMC article.
-
Association between novel PLCE1 variants identified in published esophageal cancer genome-wide association studies and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.BMC Cancer. 2011 Jun 20;11:258. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-258. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21689432 Free PMC article.
-
A variant at a potentially functional microRNA-binding site in BRIP1 was associated with risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):8057-66. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4682-6. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26711789 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms and the risk of developing a second primary cancer among head and neck cancer patients: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jun 2;21(1):660. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08335-0. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34078296 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Associations between expression levels of nucleotide excision repair proteins in lymphoblastoid cells and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Mol Carcinog. 2018 Jun;57(6):784-793. doi: 10.1002/mc.22801. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Mol Carcinog. 2018. PMID: 29528139 Free PMC article.
-
The P38α rs3804451 Variant Predicts Chemotherapy Response and Survival of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy.Transl Oncol. 2016 Dec;9(6):531-539. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2016.09.006. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Transl Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27835790 Free PMC article.
-
The Role and Function of Ras-association domain family in Cancer: A Review.Genes Dis. 2019 Jul 27;6(4):378-384. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.07.008. eCollection 2019 Dec. Genes Dis. 2019. PMID: 31832517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74–108. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30. - PubMed
-
- De Petrini M, Ritta M, Schena M, et al. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: role of the human papillomavirus in tumour progression. New Microbiol. 2006;29(1):25–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

