Molecular mechanisms of SH2- and PTB-domain-containing proteins in receptor tyrosine kinase signaling
- PMID: 24296166
- PMCID: PMC3839611
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008987
Molecular mechanisms of SH2- and PTB-domain-containing proteins in receptor tyrosine kinase signaling
Abstract
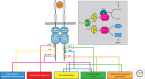
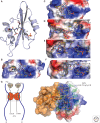
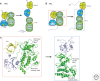
Intracellular signaling is mediated by reversible posttranslational modifications (PTMs) that include phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and acetylation, among others. In response to extracellular stimuli such as growth factors, receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) typically dimerize and initiate signaling through phosphorylation of their cytoplasmic tails and downstream scaffolds. Signaling effectors are recruited to these phosphotyrosine (pTyr) sites primarily through Src homology 2 (SH2) domains and pTyr-binding (PTB) domains. This review describes how these conserved domains specifically recognize pTyr residues and play a major role in mediating precise downstream signaling events.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson D, Koch CA, Grey L, Ellis C, Moran MF, Pawson T 1990. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase Cγ1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science 250: 979–982 - PubMed
-
- Araki T, Nawa H, Neel BG 2003. Tyrosyl phosphorylation of Shp2 is required for normal ERK activation in response to some, but not all, growth factors. J Biol Chem 278: 41677–41684 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
