Using networks to measure similarity between genes: association index selection
- PMID: 24296474
- PMCID: PMC3959882
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2728
Using networks to measure similarity between genes: association index selection
Erratum in
- Nat Methods. 2014 Mar;11(3):349
Abstract
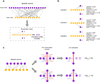
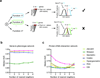
Biological networks can be used to functionally annotate genes on the basis of interaction-profile similarities. Metrics known as association indices can be used to quantify interaction-profile similarity. We provide an overview of commonly used association indices, including the Jaccard index and the Pearson correlation coefficient, and compare their performance in different types of analyses of biological networks. We introduce the Guide for Association Index for Networks (GAIN), a web tool for calculating and comparing interaction-profile similarities and defining modules of genes with similar profiles.
Figures




References
-
- Walhout AJM, et al. Protein interaction mapping in C. elegans using proteins involved in vulval development. Science. 2000;287:116–122. - PubMed
-
- Schwikowski B, Uetz P, Fields S. A network of protein-protein interactions in yeast. Nat. Genet. 2000;18:1257–1261. - PubMed
-
- Walhout AJM. Unraveling Transcription Regulatory Networks by Protein-DNA and Protein-Protein Interaction Mapping. Genome Res. 2006;16:1445–1454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

