ROS1 and ALK fusions in colorectal cancer, with evidence of intratumoral heterogeneity for molecular drivers
- PMID: 24296758
- PMCID: PMC4140177
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0479-T
ROS1 and ALK fusions in colorectal cancer, with evidence of intratumoral heterogeneity for molecular drivers
Abstract
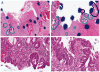
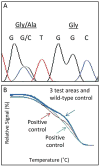
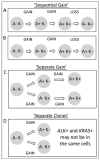
Activated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and ROS1 tyrosine kinases, through gene fusions, have been found in lung adenocarcinomas and are highly sensitive to selective kinase inhibitors. This study aimed at identifying the presence of these rearrangements in human colorectal adenocarcinoma specimens using a 4-target, 4-color break-apart FISH assay to simultaneously determine the genomic status of ALK and ROS1. Among the clinical colorectal cancer specimens analyzed, rearrangement-positive cases for both ALK and ROS1 were observed. The fusion partner for ALK was identified as EML4 and the fusion partner for one of the ROS1-positive cases was SLC34A2, the partner for the other ROS1-positive case remains to be identified. A small fraction of specimens presented duplicated or clustered copies of native ALK and ROS1. In addition, rearrangements were detected in samples that also harbored KRAS and BRAF mutations in two of the three cases. Interestingly, the ALK-positive specimen displayed marked intratumoral heterogeneity and rearrangement was also identified in regions of high-grade dysplasia. Despite the additional oncogenic events and tumor heterogeneity observed, elucidation of the first cases of ROS1 rearrangements and confirmation of ALK rearrangements support further evaluation of these genomic fusions as potential therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer.
Implications: ROS1 and ALK fusions occur in colorectal cancer and may have substantial impact in therapy selection.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008.
-
- Mitelman F, Johansson B, Mertens F. The impact of translocations and gene fusions on cancer causation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:233–45. - PubMed
-
- Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL, et al. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–4. - PubMed
-
- Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H, et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131:1190–203. - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

