Field-SEA: a model for computing the solvation free energies of nonpolar, polar, and charged solutes in water
- PMID: 24299013
- PMCID: PMC4065164
- DOI: 10.1021/jp4115139
Field-SEA: a model for computing the solvation free energies of nonpolar, polar, and charged solutes in water
Abstract
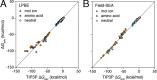
Previous work describes a computational solvation model called semi-explicit assembly (SEA). The SEA water model computes the free energies of solvation of nonpolar and polar solutes in water with good efficiency and accuracy. However, SEA gives systematic errors in the solvation free energies of ions and charged solutes. Here, we describe field-SEA, an improved treatment that gives accurate solvation free energies of charged solutes, including monatomic and polyatomic ions and model dipeptides, as well as nonpolar and polar molecules. Field-SEA is computationally inexpensive for a given solute because explicit-solvent model simulations are relegated to a precomputation step and because it represents solvating waters in terms of a solute's free-energy field. In essence, field-SEA approximates the physics of explicit-model simulations within a computationally efficient framework. A key finding is that an atom's solvation shell inherits characteristics of a neighboring atom, especially strongly charged neighbors. Field-SEA may be useful where there is a need for solvation free-energy computations that are faster than explicit-solvent simulations and more accurate than traditional implicit-solvent simulations for a wide range of solutes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Adapting the semi-explicit assembly solvation model for estimating water-cyclohexane partitioning with the SAMPL5 molecules.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2016 Nov;30(11):1067-1077. doi: 10.1007/s10822-016-9961-9. Epub 2016 Sep 8. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2016. PMID: 27632227 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling aqueous solvation with semi-explicit assembly.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 22;108(8):3234-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017130108. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21300905 Free PMC article.
-
Testing the semi-explicit assembly model of aqueous solvation in the SAMPL4 challenge.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014 Mar;28(3):259-64. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9712-8. Epub 2014 Jan 29. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014. PMID: 24474161
-
Implicit modeling of nonpolar solvation for simulating protein folding and conformational transitions.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2008 Jan 28;10(4):471-81. doi: 10.1039/b714141f. Epub 2007 Nov 14. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2008. PMID: 18183310 Review.
-
Unraveling water's entropic mysteries: a unified view of nonpolar, polar, and ionic hydration.Acc Chem Res. 2008 Aug;41(8):957-67. doi: 10.1021/ar7001478. Acc Chem Res. 2008. PMID: 18710198 Review.
Cited by
-
Using interpolation for fast and accurate calculation of ion-ion interactions.J Phys Chem B. 2014 Jul 17;118(28):8017-25. doi: 10.1021/jp501141j. Epub 2014 Mar 25. J Phys Chem B. 2014. PMID: 24625086 Free PMC article.
-
Hexahydrated Mg2+ Binding and Outer-Shell Dehydration on RNA Surface.Biophys J. 2018 Mar 27;114(6):1274-1284. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.01.040. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29590585 Free PMC article.
-
Adapting the semi-explicit assembly solvation model for estimating water-cyclohexane partitioning with the SAMPL5 molecules.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2016 Nov;30(11):1067-1077. doi: 10.1007/s10822-016-9961-9. Epub 2016 Sep 8. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2016. PMID: 27632227 Free PMC article.
-
Free-energy decomposition of salt effects on the solubilities of small molecules and the role of excluded-volume effects.Chem Sci. 2023 Nov 21;15(2):477-489. doi: 10.1039/d3sc04617f. eCollection 2024 Jan 3. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 38179544 Free PMC article.
-
Free Energy Calculations Based on Coupling Proximal Distribution Functions and Thermodynamic Cycles.J Chem Theory Comput. 2019 Apr 9;15(4):2649-2658. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.8b01157. Epub 2019 Mar 6. J Chem Theory Comput. 2019. PMID: 30768893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roux B.; Simonson T. Implicit Solvent Models. Biophys. Chem. 1999, 78, 1–20. - PubMed
-
- Feig M.; Brooks C. L. Recent Advances in the Development and Application of Implicit Solvent Models in Biomolecule Simulations. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004, 14, 217–224. - PubMed
-
- Cramer C. J.; Truhlar D. G. Implicit Solvation Models: Equilibria, Structure, Spectra, and Dynamics. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2161–2200. - PubMed
-
- Villa A.; Mark A. E. Calculation of the Free Energy of Solvation for Neutral Analogs of Amino Acid Side Chains. J. Comput. Chem. 2002, 23, 548–553. - PubMed
-
- Shirts M. R.; Pitera J. W.; Swope W. C.; Pande V. S. Extremely Precise Free Energy Calculations of Amino Acid Side Chain Analogs: Comparison of Common Molecular Mechanics Force Fields for Proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 5740–5761.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

