Q wave area for stratification of global left ventricular infarct size: comparison to conventional ECG assessment using Selvester QRS-score
- PMID: 24300167
- PMCID: PMC3940061
- DOI: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000062
Q wave area for stratification of global left ventricular infarct size: comparison to conventional ECG assessment using Selvester QRS-score
Abstract
Objectives: Left ventricular (LV) infarct size is a prognostic determinant after acute myocardial infarction (AMI). ECG data have been used to measure infarct size, but conventional approaches use multiparametric algorithms that have limited clinical applicability. This study tested a novel ECG approach - based solely on Q wave area - for calculation of LV infarct size.
Methods: Serial 12-lead ECGs were performed in AMI patients. Computerized software was used to quantify Q wave area (summed across surface ECG leads) and Selvester QRS-score components. ECG analysis was compared to the reference of myocardial infarct size quantified by delayed enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance.
Results: Overall, 158 patients underwent ECG during early (4±0.4) and follow-up (29±5 days) post-AMI time points. Selvester QRS-score and Q wave area increased stepwise with LV infarct size (P<0.001). Whereas both methods manifested marked increases at a threshold of 10% LV infarction, magnitude was greater for Q wave area (>2.5-fold) than Selvester QRS-score (<two-fold). In receiver operating characteristic analysis, Q wave area (area under the curve=0.83-0.86) and Selvester QRS-score (0.82-0.87) manifested similar performance in relation to a 10% infarct cutoff. When Selvester QRS-score and Q wave area thresholds were selected to optimize sensitivity, both methods yielded similar negative predictive value (Q wave area: 89-91%, Selvester QRS-score: 92-94%) although specificity was higher for Q wave area (44-45 vs. 17-25%; P≤0.01).
Conclusion: Q wave area provides an index for stratification of LV infarct size that performs similarly to conventional ECG assessment via the Selvester QRS-score for exclusion of large infarction.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00539045.
Figures
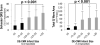


References
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons ML, Chaitman BR, White HD. on behalf of the Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1581–1598. - PubMed
-
- Selvester RH, Wagner GS, Hindman NB. The selvester qrs scoring system for estimating myocardial infarct size. The development and application of the system. Arch Intern Med. 1985;145:1877–1881. - PubMed
-
- Bang LE, Ripa RS, Grande P, Kastrup J, Clemmensen PM, Wagner GS. Comparison of infarct size changes with delayed contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and electrocardiogram qrs scoring during the 6 months after acutely reperfused myocardial infarction. J Electrocardiol. 2008;41:609–613. - PubMed
-
- Carlsen EA, Bang LE, Ahtarovski KA, Engstrom T, Kober L, Kelbaek H, et al. Comparison of selvester qrs score with magnetic resonance imaging measured infarct size in patients with st elevation myocardial infarction. J Electrocardiol. 2012;45:414–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

