Expression Profile of Drug and Nutrient Absorption Related Genes in Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) Cells Grown under Differentiation Conditions
- PMID: 24300234
- PMCID: PMC3834914
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics4020314
Expression Profile of Drug and Nutrient Absorption Related Genes in Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) Cells Grown under Differentiation Conditions
Abstract
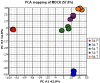
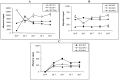
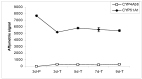
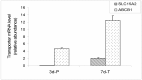
The expression levels of genes involved in drug and nutrient absorption were evaluated in the Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) in vitro drug absorption model. MDCK cells were grown on plastic surfaces (for 3 days) or on Transwell® membranes (for 3, 5, 7, and 9 days). The expression profile of genes including ABC transporters, SLC transporters, and cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes was determined using the Affymetrix® Canine GeneChip®. Expression of genes whose probe sets passed a stringent confirmation process was examined. Expression of a few transporter (MDR1, PEPT1 and PEPT2) genes in MDCK cells was confirmed by RT-PCR. The overall gene expression profile was strongly influenced by the type of support the cells were grown on. After 3 days of growth, expression of 28% of the genes was statistically different (1.5-fold cutoff, p < 0.05) between the cells grown on plastic and Transwell® membranes. When cells were differentiated on Transwell® membranes, large changes in gene expression profile were observed during the early stages, which then stabilized after 5-7 days. Only a small number of genes encoding drug absorption related SLC, ABC, and CYP were detected in MDCK cells, and most of them exhibited low hybridization signals. Results from this study provide valuable reference information on endogenous gene expression in MDCK cells that could assist in design of drug-transporter and/or drug-enzyme interaction studies, and help interpret the contributions of various transporters and metabolic enzymes in studies with MDCK cells.
Figures

References
-
- Sun D., Lennernas H., Welage L.S., Barnett J.L., Landowski C.P., Foster D., Fleisher D., Lee K.D., Amidon G.L. Comparison of human duodenum and caco-2 gene expression profiles for 12,000 gene sequences tags and correlation with permeability of 26 drugs. Pharm. Res. 2002;19:1400–1416. doi: 10.1023/A:1020483911355. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sambuy Y., De Angelis I., Ranaldi G., Scarino M.L., Stammati A., Zucco F. The caco-2 cell line as a model of the intestinal barrier: Influence of cell and culture-related factors on caco-2 cell functional characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005;21:1–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

