Cardiolipin asymmetry, oxidation and signaling
- PMID: 24300280
- PMCID: PMC3973441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.11.010
Cardiolipin asymmetry, oxidation and signaling
Abstract
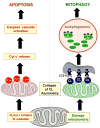
Cardiolipins (CLs) are ancient and unusual dimeric phospholipids localized in the plasma membrane of bacteria and in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes. In mitochondria, two types of asymmetries--trans-membrane and molecular--are essential determinants of CL functions. In this review, we describe CL-based signaling mitochondrial pathways realized via modulation of trans-membrane asymmetry and leading to externalization and peroxidation of CLs in mitophagy and apoptosis, respectively. We discuss possible mechanisms of CL translocations from the inner leaflet of the inner to the outer leaflet of the outer mitochondrial membranes. We present redox reaction mechanisms of cytochrome c-catalyzed CL peroxidation as a required stage in the execution of apoptosis. We also emphasize the significance of CL-related metabolic pathways as new targets for drug discovery. Finally, a remarkable diversity of polyunsaturated CL species and their oxidation products have evolved in eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes. This diversity--associated with CL molecular asymmetry--is presented as the basis for mitochondrial communications language.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cardiolipin; Cardiolipin asymmetry; Cardiolipin oxidation mitochondria; Mitophagy.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
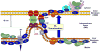
References
-
- Ardail D, Privat JP, Egret-Charlier M, Levrat C, Lerme F, Louisot P. Mitochondrial contact sites. Lipid composition and dynamics. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1990;265:18797–18802. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson J, Kapralov AA, Yanamala N, Tyurina YY, Amoscato AA, Pearce L, Peterson J, Huang Z, Jiang J, Samhan-Arias AK, Maeda A, Feng W, Wasserloos K, Belikova NA, Tyurin VA, Wang H, Fletcher J, Wang Y, Vlasova II, Klein-Seetharaman J, Stoyanovsky DA, Bayir H, Pitt BR, Epperly MW, Greenberger JS, Kagan VE. A mitochondria-targeted inhibitor of cytochrome c peroxidase mitigates radiation-induced death. Nature communications. 2011;2:497. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1499. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basova LV, Kurnikov IV, Wang L, Ritov VB, Belikova NA, Vlasova II, Pacheco AA, Winnica DE, Peterson J, Bayir H, Waldeck DH, Kagan VE. Cardiolipin switch in mitochondria: shutting off the reduction of cytochrome c and turning on the peroxidase activity. Biochemistry. 2007;46:3423–3434. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL070755/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 OH008282/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- U19 AI068021/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NS065789/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG026389/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ES021068/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS061817/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS076511/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ES020693/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL094488/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS065789/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS076511/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026389/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES021068/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- NS061817/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065789/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES020693/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- OH008282/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- R01 NS061817/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

