Hypothalamic astroglial connexins are required for brain glucose sensing-induced insulin secretion
- PMID: 24301293
- PMCID: PMC3915215
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.206
Hypothalamic astroglial connexins are required for brain glucose sensing-induced insulin secretion
Abstract
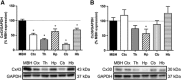
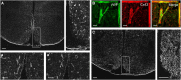
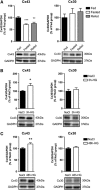
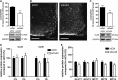
Hypothalamic glucose detection participates in maintaining glycemic balance, food intake, and thermogenesis. Although hypothalamic neurons are the executive cells involved in these responses, there is increasing evidence that astrocytes participate in glucose sensing (GS); however, it is unknown whether astroglial networking is required for glucose sensitivity. Astroglial connexins 30 and 43 (Cx30 and Cx43) form hexameric channels, which are apposed in gap junctions, allowing for the intercellular transfer of small molecules such as glucose throughout the astroglial networks. Here, we hypothesized that hypothalamic glucose sensitivity requires these connexins. First, we showed that both Cxs are enriched in the rat hypothalamus, with highly concentrated Cx43 expression around blood vessels of the mediobasal hypothalamus (MBH). Both fasting and high glycemic levels rapidly altered the protein levels of MBH astroglial connexins, suggesting cross talk within the MBH between glycemic status and the connexins' ability to dispatch glucose. Finally, the inhibition of MBH Cx43 (by transient RNA interference) attenuated hypothalamic glucose sensitivity in rats, which was demonstrated by a pronounced decreased insulin secretion in response to a brain glucose challenge. These results illustrate that astroglial connexins contribute to hypothalamic GS.
Figures

References
-
- Blouet C, Schwartz GJ. Hypothalamic nutrient sensing in the control of energy homeostasis. Behav Brain Res. 2010;209:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Lam TKT, Gutierrez-Juarez R, Pocai A, Rossetti L. Regulation of blood glucose by hypothalamic pyruvate metabolism. Science. 2005;309:943–947. - PubMed
-
- Leloup C, Magnan C, Benani A, Bonnet E, Alquier T, Offer G, et al. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species are required for hypothalamic glucose sensing. Diabetes. 2006;55:2084–2090. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi T, Bray Ga. The effect of intrahypothalamic injections of glucose on sympathetic efferent firing rate. Brain Res Bull. 1987;18:591–595. - PubMed
-
- Fioramonti X, Contié S, Song Z, Routh VH, Lorsignol A, Pénicaud L. Characterization of glucosensing neuron subpopulations in the arcuate nucleus: integration in neuropeptide Y and pro-opio melanocortin networks. Diabetes. 2007;56:1219–1227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

