PPARα activation can help prevent and treat non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 24302581
- PMCID: PMC3902646
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1928
PPARα activation can help prevent and treat non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
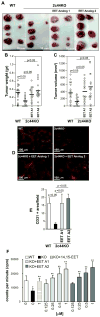
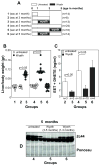
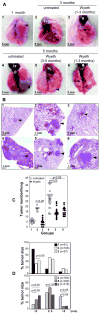
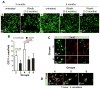
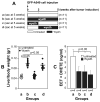
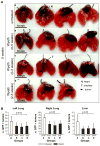
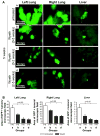
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) not amenable to surgical resection has a high mortality rate, due to the ineffectiveness and toxicity of chemotherapy. Thus, there remains an urgent need of efficacious drugs that can combat this disease. In this study, we show that targeting the formation of proangiogenic epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EET) by the cytochrome P450 arachidonic acid epoxygenases (Cyp2c) represents a new and safe mechanism to treat NSCLC growth and progression. In the transgenic murine K-Ras model and human orthotopic models of NSCLC, we found that Cyp2c44 could be downregulated by activating the transcription factor PPARα with the ligands bezafibrate and Wyeth-14,643. Notably, both treatments reduced primary and metastatic NSCLC growth, tumor angiogenesis, endothelial Cyp2c44 expression, and circulating EET levels. These beneficial effects were independent of the time of administration, whether before or after the onset of primary NSCLC, and they persisted after drug withdrawal, suggesting the benefits were durable. Our findings suggest that strategies to downregulate Cyp2c expression and/or its enzymatic activity may provide a safer and effective strategy to treat NSCLC. Moreover, as bezafibrate is a well-tolerated clinically approved drug used for managing lipidemia, our findings provide an immediate cue for clinical studies to evaluate the utility of PPARα ligands as safe agents for the treatment of lung cancer in humans.
Figures
References
-
- Walker S. Updates in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2008;12:587–96. - PubMed
-
- Berman AT, Rengan R. New approaches to radiotherapy as definitive treatment for inoperable lung cancer. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;20:188–97. - PubMed
-
- Patel S, Sanborn RE, Thomas CR., Jr Definitive chemoradiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer with N2 disease. Thorac Surg Clin. 2008;18:393–401. - PubMed
-
- Cabebe E, Wakelee H. Role of anti-angiogenesis agents in treating NSCLC: focus on bevacizumab and VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2007;8:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Fernando NT, Koch M, Rothrock C, Gollogly LK, D’Amore PA, Ryeom S, et al. Tumor escape from endogenous, extracellular matrix-associated angiogenesis inhibitors by up-regulation of multiple proangiogenic factors. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1529–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-DK095761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069921/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002025/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R25 GM062459/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083187/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5P50 CA-090949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA162433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK083187/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK075594/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002196/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P01 DK038226/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK383069221/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA162433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075594/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

