SMG-ly knocking out gene expression in specific cells: an educational primer for use with "a novel strategy for cell-autonomous gene knockdown in caenorhabditis elegans defines a cell-specific function for the G-protein subunit GOA-1"
- PMID: 24302743
- PMCID: PMC3832266
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.113.157701
SMG-ly knocking out gene expression in specific cells: an educational primer for use with "a novel strategy for cell-autonomous gene knockdown in caenorhabditis elegans defines a cell-specific function for the G-protein subunit GOA-1"
Abstract
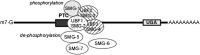
A recent article by Maher et al. in GENETICS introduces an alternative approach to cell-type-specific gene knockdown in Caenorhabditis elegans, using nonsense-mediated decay. This strategy has the potential to be applicable to other organisms (this strategy requires that animals can survive without nonsense-mediated decay-not all can). This Primer article provides a guide and resource for educators and students by describing different gene knockdown methodologies, by assisting with the technically difficult portions of the Maher et al. article, and by providing conceptual questions relating to the article.
Keywords: cell-specific gene expression; education; nonsense-mediated decay (NMD).
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel strategy for cell-autonomous gene knockdown in Caenorhabditis elegans defines a cell-specific function for the G-protein subunit GOA-1.Genetics. 2013 Jun;194(2):363-73. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.149724. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23525334 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization of smg-8 mutants reveals no role in C. elegans nonsense mediated decay.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049490. Epub 2012 Nov 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166684 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of novel factors that act in the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway in nematodes, flies and mammals.EMBO Rep. 2015 Jan;16(1):71-8. doi: 10.15252/embr.201439183. Epub 2014 Dec 1. EMBO Rep. 2015. PMID: 25452588 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotrimeric G proteins in C. elegans.WormBook. 2006 Oct 13:1-25. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.75.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18050432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic analysis of RGS protein function in Caenorhabditis elegans.Methods Enzymol. 2004;389:305-20. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(04)89018-9. Methods Enzymol. 2004. PMID: 15313573 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinformat-Eggs: An Educational Primer for Use with "LIN-41 and OMA Ribonucleoprotein Complexes Mediate a Translational Repression-to-Activation Switch Controlling Oocyte Meiotic Maturation and the Oocyte-to-Embryo Transition in Caenorhabditis elegans".Genetics. 2018 Jul;209(3):675-683. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301139. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29967060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarado A. S., 2003. The freshwater planarian Schmidtea mediterranea: embryogenesis, stem cells, and regeneration. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 13: 438–444. - PubMed
-
- Boutros M., Ahringer J., 2008. The art and design of genetic screens: RNA interference. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9: 554–566. - PubMed
-
- Capecchi M. R., 2005. Gene targeting in mice: functional analysis of the mammalian genome for the twenty-first century. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6: 507–512. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y. F., Imam J. S., Wilkinson M. F., 2007. The nonsense-mediated RNA surveillance pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76: 51–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

