Lupeol is one of active components in the extract of Chrysanthemum indicum Linne that inhibits LMP1-induced NF-κB activation
- PMID: 24303085
- PMCID: PMC3841202
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082688
Lupeol is one of active components in the extract of Chrysanthemum indicum Linne that inhibits LMP1-induced NF-κB activation
Abstract
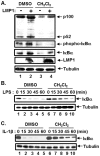
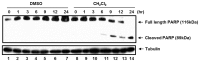
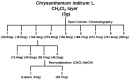
We have previously reported that seventy percent ethanol extract of Chrysanthemum indicum Linne (CIE) strongly reduces Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed lymphoblastoid cell line (LCL) survival by inhibiting virus-encoded latent infection membrane protein 1 (LMP1)-induced NF-κB activation. To identify an active compound(s) in CIE that inhibits LMP1-induced NF-κB activation, activity-guided fractionation was employed. The CH2Cl2 fraction of CIE strongly reduced LMP1-induced NF-κB activation and LCL viability with relatively low cytotoxic effects on primary human foreskin fibroblast (HFF), HeLa or Burkitt's lymphoma (BL41) cells. Furthermore, lupeol, a pentacyclic triterpene, was identified in the CH2Cl2 fraction of CIE to attenuate LMP1-induced NF-κB activation and LCL viability. This study demonstrates that lupeol is one of active compounds in the CH2Cl2 fraction of CIE that inhibits LMP1-induced NF-κB activation and reduces NF-κB-dependent LCL viability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

