Benefits of omega-3 fatty acid against bone changes in salt-loaded rats: possible role of kidney
- PMID: 24303178
- PMCID: PMC3841042
- DOI: 10.1002/phy2.106
Benefits of omega-3 fatty acid against bone changes in salt-loaded rats: possible role of kidney
Abstract
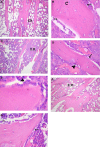
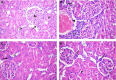
There is evidence that dietary fats are important components contributing in bone health and that bone mineral density is inversely related to sodium intake. Salt loading is also known to impose negative effects on renal function. The present study aimed to determine the effect of the polyunsaturated fatty acid omega-3 on bone changes imposed by salt loading, highlighting the role of kidney as a potential mechanism involved in this effect. Male Wistar rats were divided into three groups: control group, salt-loaded group consuming 2% NaCl solution as drinking water for 8 weeks, and omega-3-treated salt-loaded group receiving 1 g/kg/day omega-3 by gavage with consumption of 2% NaCl solution for 8 weeks. Systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and heart rate (HR) were recorded. Plasma levels of sodium, potassium, calcium, inorganic phosphorus (Pi), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), creatinine, urea, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D3], and transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) were measured. The right tibia and kidney were removed for histologic examination and renal immunohistochemical analysis for endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) was performed. The results revealed that omega-3 reduced SBP, DBP, and MAP and plasma levels of sodium, potassium, Pi, creatinine, urea, and TGF-β1, but increased plasma levels of calcium, ALP, and 1,25(OH)2D3 as well as renal eNOS. Omega-3 increased cortical and trabecular bone thickness, decreased osteoclast number, and increased newly formed osteoid bone. Renal morphology was found preserved. In conclusion, omega-3 prevents the disturbed bone status imposed by salt loading. This osteoprotective effect is possibly mediated by attenuation of alterations in Ca(2+), Pi, and ALP, and improvement of renal function and arterial blood pressure.
Keywords: Bone; omega-3; renal function; salt intake.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective effects of AT1-receptor blocker and CA antagonist combination on renal function in salt loaded spontaneously hypertensive rats.Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2015;36(1):85-91. Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2015. PMID: 26076778
-
Effect of salt loading on baroreflex sensitivity in reduced renal mass hypertension.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017;39(7):592-600. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2017.1299748. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28635325
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents salt sensitivity in diabetic rats and decreases oxidative stress.Nutrition. 2020 Apr;72:110644. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2019.110644. Epub 2019 Nov 23. Nutrition. 2020. PMID: 32044546
-
Dietary treatment of urinary risk factors for renal stone formation. A review of CLU Working Group.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015 Jul 7;87(2):105-20. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2015.2.105. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015. PMID: 26150027 Review.
-
Vitamin D and type II sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters.Contrib Nephrol. 2013;180:86-97. doi: 10.1159/000346786. Epub 2013 May 6. Contrib Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23652552 Review.
Cited by
-
CKD-MBD post kidney transplantation.Pediatr Nephrol. 2021 Jan;36(1):41-50. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04421-5. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 31858226
-
Optimization of Bone Health in Children before and after Renal Transplantation: Current Perspectives and Future Directions.Front Pediatr. 2014 Feb 24;2:13. doi: 10.3389/fped.2014.00013. eCollection 2014. Front Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24605319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective effect of omega-3 fatty acids on spinal cord injury induced rats.Brain Behav. 2019 Aug;9(8):e01339. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1339. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 31225705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An WS, Kim HJ, Cho KH, Vaziri ND. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in the remnant kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009;297:F895–F903. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft JB, Gamble M. Theory and practice of histological techniques. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier; 2008.
-
- Barcelli UO, Miyata J, Ito Y, Gallon L, Laskarzewski P, Weiss M, et al. Beneficial effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids in partially nephrectomized rats. Prostaglandins. 1986;32:211–219. - PubMed
-
- Barsanti JA, Pillsbury HR, III, Freis ED. Enhanced salt toxicity in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1971;136:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Bover J, Jara A, Trinidad P, Rodriguez M, Felsenfeld AJ. Dynamics of skeletal resistance to parathyroid hormone in the rat: effect of renal failure and dietary phosphorus. Bone. 1999;25:279–285. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

