Combined intratympanic and systemic steroid therapy for poor-prognosis sudden sensorineural hearing loss
- PMID: 24303415
- PMCID: PMC3846240
Combined intratympanic and systemic steroid therapy for poor-prognosis sudden sensorineural hearing loss
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of combined intratympanic and systemic steroid therapy compared with systemic steroid therapy alone in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) patients with poor prognostic factors.
Materials and methods: Seventy-seven patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) who had at least one poor prognostic factor (age greater than 40 years, hearing loss more than 70 db, or greater than a 2-week delay between the onset of hearing loss and initiation of therapy) were included in this study. Patients were randomized to the intervention group (combined intratympanic and systemic steroid therapy) or the control group (systemic steroid therapy alone). All patients received oral treatment with systemic prednisolone (1 mg/kg/day for 10 days), acyclovir (2 g/day for 10 days, divided into four doses), triamterene H (daily), and omeprazole (daily, during steroid treatment), and were advised to follow a low salt diet. The intervention group also received intratympanic dexamethasone injections (0.4 ml of 4 mg/ml dexamethasone) two times a week for two consecutive weeks (four injections in total). A significant hearing improvement was defined as at least a 15-db decrease in pure tone average (PTA).
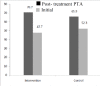
Results: Among all participants,44 patients(57.14%) showed significant improvement in hearing evaluation. More patients showed hearing improvement in the intervention group than in the control group (27 patients (75%) versus 17 patients (41.4%), respectively; P=0.001).
Conclusion: The combination of intratympanic dexamethasone and systemic prednisolone is more effective than systemic prednisolone alone in the treatment of poor-prognosis SSNHL.
Keywords: Intratympanic Dexamethasone; Sudden deafness; Sudden hearing loss.
Figures
References
-
- Seggas I, Koltsidopoulos P, Bibas A, Tzonou A, Sismanis A. Intratympanic steroid therapy for sudden hearing loss: A review of literature. Otol Neurotol . 2011;32(1):29–35. - PubMed
-
- Westerlaken BO, de Kleine E, van der Laan B, Albers F. The treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss using pulse therapy: A prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(4):684–90. - PubMed
-
- Plaza G, Herraiz C. Intratympanic steroids for treatment of sudden hearing loss after failure of intravenous therapy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;137(1):74–8. - PubMed
-
- Conlin AE, Parnes LS. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss, a systematic review. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133(6):573–81. - PubMed
-
- Quaranta N, Ramunni A, Brescia P, D’Elia A, Vacca A, Ria R. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 in sudden hearing loss. Otol Neurotol. 2008;29(4):470–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous