α₁ adrenoceptor activation by norepinephrine inhibits LPS-induced cardiomyocyte TNF-α production via modulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 24304472
- PMCID: PMC3930413
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12184
α₁ adrenoceptor activation by norepinephrine inhibits LPS-induced cardiomyocyte TNF-α production via modulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathway
Abstract
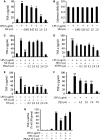
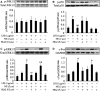
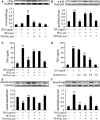
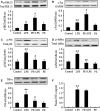
Cardiomyocyte tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) production contributes to myocardial depression during sepsis. This study was designed to observe the effect of norepinephrine (NE) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cardiomyocyte TNF-α expression and to further investigate the underlying mechanisms in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and endotoxaemic mice. In cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, NE inhibited LPS-induced TNF-α production in a dose-dependent manner. α₁- adrenoceptor (AR) antagonist (prazosin), but neither β₁- nor β₂-AR antagonist, abrogated the inhibitory effect of NE on LPS-stimulated TNF-α production. Furthermore, phenylephrine (PE), an α₁-AR agonist, also suppressed LPS-induced TNF-α production. NE inhibited p38 phosphorylation and NF-κB activation, but enhanced extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation and c-Fos expression in LPS-treated cardiomyocytes, all of which were reversed by prazosin pre-treatment. To determine whether ERK1/2 regulates c-Fos expression, p38 phosphorylation, NF-κB activation and TNF-α production, cardiomyocytes were also treated with U0126, a selective ERK1/2 inhibitor. Treatment with U0126 reversed the effects of NE on c-Fos expression, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation and TNF-α production, but not NF-κB activation in LPS-challenged cardiomyocytes. In addition, pre-treatment with SB202190, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, partly inhibited LPS-induced TNF-α production in cardiomyocytes. In endotoxaemic mice, PE promoted myocardial ERK1/2 phosphorylation and c-Fos expression, inhibited p38 phosphorylation and IκBα degradation, reduced myocardial TNF-α production and prevented LPS-provoked cardiac dysfunction. Altogether, these findings indicate that activation of α₁-AR by NE suppresses LPS-induced cardiomyocyte TNF-α expression and improves cardiac dysfunction during endotoxaemia via promoting myocardial ERK phosphorylation and suppressing NF-κB activation.
Keywords: Lipopolysaccharide; Tumour necrosis factor-α; cardiomyocytes; α1-adrenoceptor.
© 2013 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Zhang T, Feng Q. Nitric oxide and calcium signaling regulate myocardial tumor necrosis factor-α expression and cardiac function in sepsis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;88:92–104. - PubMed
-
- Cain BS, Meldrum DR, Dinarello CA, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta synergistically depress human myocardial function. Crit Care Med. 1999;27:1309–18. - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, Bakker J, Marécaux G, et al. Administration of anti-TNF antibody improves left ventricular function in septic shock patients. Results of a pilot study. Chest. 1992;101:810–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

