Attenuated dopaminergic tone in the paraventricular nucleus contributing to sympathoexcitation in rats with Type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 24305061
- PMCID: PMC3921316
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00323.2013
Attenuated dopaminergic tone in the paraventricular nucleus contributing to sympathoexcitation in rats with Type 2 diabetes
Abstract
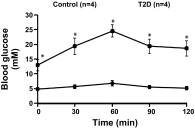
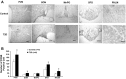
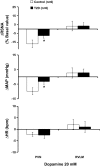
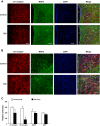
The study was conducted to investigate the role for dopamine in the centrally mediated sympathoexcitatory response in rats with Type 2 diabetes (T2D). T2D was induced by a combination of high-fat diet (HFD) and low-dose streptozotocin (STZ). HFD/STZ treatment for 12-14 wk resulted in significant increase in the number of FosB-positive cells in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM). In anesthetized rats, administration of exogenous dopamine (dopamine hydrochloride, 20 mM) in the PVN, but not in the RVLM, elicited decreases in renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) in control rats and but not in the T2D rats. Blocking the endogenous dopamine with dopamine D1/D5 receptor antagonist SCH39166 (2 mM) in the PVN and RVLM, resulted in increases in RSNA, MAP, and heart rate (HR) in both control and T2D rats. These responses were significantly attenuated in T2D rats compared with control rats (PVN - ΔRSNA: 21 ± 10 vs. 44 ± 2%; ΔMAP: 7 ± 3 vs. 19 ± 6 mmHg, ΔHR: 17 ± 5 vs. 32 ± 4 bpm, P < 0.05). There were no significant increases in response to dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist raclopride application in the PVN and RVLM of both control and T2D rats. Furthermore, there were decreased dopamine D1 receptor and D2 receptor expressions in the PVN of T2D rats. Taken together, these data suggest that reduced endogenous dopaminergic tone within the PVN may contribute to the sympathoexcitation in T2D.
Keywords: central nervous system; dopaminergic; sympathetic nerve activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sympathoexcitation by hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons projecting to the rostral ventrolateral medulla.J Physiol. 2018 Oct;596(19):4581-4595. doi: 10.1113/JP276223. Epub 2018 Aug 18. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30019338 Free PMC article.
-
Sympathoexcitatory input from hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons projecting to rostral ventrolateral medulla is enhanced after myocardial infarction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):H1197-H1207. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00273.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32946261
-
Beneficial effects of metformin supplementation in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and arcuate nucleus of type 2 diabetic rats.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 15;437:115893. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.115893. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35085591
-
Salusin-β in paraventricular nucleus increases blood pressure and sympathetic outflow via vasopressin in hypertensive rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Jun 1;98(3):344-51. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt031. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23400761
-
Integration of renal sensory afferents at the level of the paraventricular nucleus dictating sympathetic outflow.Auton Neurosci. 2017 May;204:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2016.08.008. Epub 2016 Aug 6. Auton Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27527558 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Cell Excitability of Cardiac Postganglionic Parasympathetic Neurons Correlates With Myocardial Infarction-Induced Fatal Ventricular Arrhythmias in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Neurosci. 2021 Aug 18;15:721364. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.721364. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34483832 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian-timed quick-release bromocriptine lowers elevated resting heart rate in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2019 Nov 13;3(1):e00101. doi: 10.1002/edm2.101. eCollection 2020 Jan. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2019. PMID: 31922028 Free PMC article.
-
A novel role for dopamine signaling in the pathogenesis of bone loss from the atypical antipsychotic drug risperidone in female mice.Bone. 2017 Oct;103:168-176. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Bone. 2017. PMID: 28689816 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental dopaminergic neuron lesion at the area of the biological clock pacemaker, suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) induces metabolic syndrome in rats.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021 Jan 23;13(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13098-021-00630-x. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 33485386 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroendocrine circuits governing energy balance and stress regulation: functional overlap and therapeutic implications.Cell Metab. 2014 Jun 3;19(6):910-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.01.020. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Cell Metab. 2014. PMID: 24630812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ao Y, Ko M, Chen A, Marvizon JC, Adelson D, Song MK, Go VL, Liu YY, Yang H. Potent hyperglycemic and hyperinsulinemic effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone microinjected into the rostroventrolateral medulla and abnormal responses in type 2 diabetic rats. Neuroscience 169: 706–719, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Card JP, Sved JC, Craig B, Raizada M, Vazquez J, Sved AF. Efferent projections of rat rostroventrolateral medulla C1 catecholamine neurons: Implications for the central control of cardiovascular regulation. J Comp Neurol 499: 840–859, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Dampney RA. The subretrofacial vasomotor nucleus: Anatomical, chemical and pharmacological properties and role in cardiovascular regulation. Prog Neurobiol 42: 197–227, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Dearry A, Gingrich JA, Palardeai P, Fremeau RT, Jr, Bates MD, Caron MG. Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor. Nature 347: 72–76, 1990 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

