Inflammatory myopathies
- PMID: 24305450
- PMCID: PMC10563959
- DOI: 10.1212/01.CON.0000440662.26427.bd
Inflammatory myopathies
Abstract
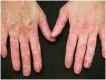
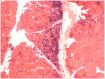
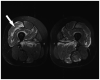
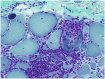
Purpose of review: To discuss the clinical, laboratory, and histopathologic features and presumed pathogenic mechanisms of the four major categories of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy, namely dermatomyositis, polymyositis, immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy, and inclusion body myositis.
Recent findings: Dermatomyositis, polymyositis, necrotizing myopathy, and inclusion body myositis are clinically, histologically, and pathogenically distinct. Polymyositis is a T cell-mediated disorder directed against muscle fibers. The pathogenesis of dermatomyositis, necrotizing myopathy, and inclusion body myositis are unknown. Dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and necrotizing myopathy are generally, but not always, responsive to immunosuppressive therapy, in contrast to inclusion body myositis, which is generally refractory to therapy.
Summary: The pattern of muscle weakness, other clinical features (eg, rash, concurrent interstitial lung disease), laboratory features (creatine kinase, autoantibodies), and muscle biopsies are useful in distinguishing subtypes of inflammatory myopathy and in guiding treatment. More research is necessary to unravel the exact pathogenic bases of these myopathies and identify better treatments.
Figures


References
-
- Amato AA,, Barohn RJ. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Neurol Clin 1997; 15 (3): 615–648. - PubMed
-
- Amato AA,, Barohn RJ. Evaluation and treatment of inflammatory myopathies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009; 80 (10): 1060–1068. - PubMed
-
- Amato AA,, Barohn RJ. Inclusion body myositis: old and new concepts. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009; 80 (11): 1186–1193. - PubMed
-
- Amato AA,, Gronseth GS,, Jackson CE, et al. Inclusion body myositis: clinical and pathological boundaries. Ann Neurol 1996; 40 (4): 581–586. - PubMed
-
- Amato AA,, Russell J. Neuromuscular disease. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
