Haploid genomes illustrate epigenetic constraints and gene dosage effects in mammals
- PMID: 24305551
- PMCID: PMC4175507
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8935-6-41
Haploid genomes illustrate epigenetic constraints and gene dosage effects in mammals
Abstract
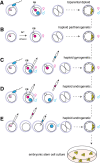
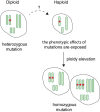
Sequencing projects have revealed the information of many animal genomes and thereby enabled the exploration of genome evolution. Insights into how genomes have been repeatedly modified provide a basis for understanding evolutionary innovation and the ever increasing complexity of animal developmental programs. Animal genomes are diploid in most cases, suggesting that redundant information in two copies of the genome increases evolutionary fitness. Genomes are well adapted to a diploid state. Changes of ploidy can be accommodated early in development but they rarely permit successful development into adulthood. In mammals, epigenetic mechanisms including imprinting and X inactivation restrict haploid development. These restrictions are relaxed in an early phase of development suggesting that dosage regulation appears less critical. Here we review the recent literature on haploid genomes and dosage effects and try to embed recent findings in an evolutionary perspective.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Haploid animal cells.Development. 2014 Apr;141(7):1423-6. doi: 10.1242/dev.102202. Development. 2014. PMID: 24644259 Review.
-
A comparative analysis of methods for de novo assembly of hymenopteran genomes using either haploid or diploid samples.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 24;9(1):6480. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42795-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31019201 Free PMC article.
-
Haploid mouse embryonic stem cells: rapid genetic screening and germline transmission.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:705-22. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100913-012920. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25288120 Review.
-
Evolution of haploid-diploid life cycles when haploid and diploid fitnesses are not equal.Evolution. 2017 Feb;71(2):215-226. doi: 10.1111/evo.13125. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Evolution. 2017. PMID: 27859032
-
Evolution of haploid selection in predominantly diploid organisms.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 29;112(52):15952-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512004112. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26669442 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A versatile genetic tool: haploid cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Sep 29;8(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0657-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28962667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of ploidy and sex-locus genotype on gene expression patterns in the fire ant Solenopsis invicta.Proc Biol Sci. 2014 Dec 22;281(1797):20141776. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.1776. Proc Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25355475 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinting as Basis for Complex Evolutionary Novelties in Eutherians.Biology (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;13(9):682. doi: 10.3390/biology13090682. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Haploidy-linked cell proliferation defects limit larval growth in zebrafish.Open Biol. 2024 Oct;14(10):240126. doi: 10.1098/rsob.240126. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 39378986 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

