MAKER-P: a tool kit for the rapid creation, management, and quality control of plant genome annotations
- PMID: 24306534
- PMCID: PMC3912085
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.230144
MAKER-P: a tool kit for the rapid creation, management, and quality control of plant genome annotations
Abstract
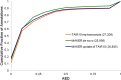
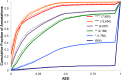
We have optimized and extended the widely used annotation engine MAKER in order to better support plant genome annotation efforts. New features include better parallelization for large repeat-rich plant genomes, noncoding RNA annotation capabilities, and support for pseudogene identification. We have benchmarked the resulting software tool kit, MAKER-P, using the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) and maize (Zea mays) genomes. Here, we demonstrate the ability of the MAKER-P tool kit to automatically update, extend, and revise the Arabidopsis annotations in light of newly available data and to annotate pseudogenes and noncoding RNAs absent from The Arabidopsis Informatics Resource 10 build. Our results demonstrate that MAKER-P can be used to manage and improve the annotations of even Arabidopsis, perhaps the best-annotated plant genome. We have also installed and benchmarked MAKER-P on the Texas Advanced Computing Center. We show that this public resource can de novo annotate the entire Arabidopsis and maize genomes in less than 3 h and produce annotations of comparable quality to those of the current The Arabidopsis Information Resource 10 and maize V2 annotation builds.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

