Endovenous saphenous vein ablation in patients with acute isolated superficial-vein thrombosis
- PMID: 24307241
- PMCID: PMC4390523
- DOI: 10.1177/0268355513514047
Endovenous saphenous vein ablation in patients with acute isolated superficial-vein thrombosis
Abstract
Objective: The possible benefits of endovenous saphenous ablation (EVSA) as initial treatment in patients presenting with isolated superficial-vein thrombosis (SVT) and saphenous vein reflux include: (1) definitive treatment of the underlying pathology and (2) elimination of the saphenous vein as a path for pulmonary emboli, which (3) may eliminate the need for anticoagulation.
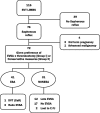
Methods: In a ten-year review of 115 limbs presenting with acute isolated SVT, 72 limbs (71 patients) with saphenous reflux were given a choice of two treatments following an explanation of the risks and benefits of each. Group I limbs (n = 41) were treated with office EVSA using radiofrequency or laser with or without thrombophlebectomy if performed within 45 days of diagnosis. Post-treatment anticoagulants were not given. Group II limbs (n = 31) were treated with compression hose and repeat Duplex within one week, with added anticoagulants if SVT extended into the thigh.
Results: In group I, mean interval from diagnosis to treatment was 13.7 days. One calf deep vein thrombosis was noted. In group II no complications were noted. In late follow-up of group II patients, 12/29 underwent EVSA more than 45 days after initial presentation.
Conclusions: The safety and efficacy of EVSA and thrombophlebectomy appear indistinguishable from conservative measures and may be offered as initial treatment to patients presenting with SVT and saphenous reflux.
Keywords: Saphenous vein ablation; phlebectomy; saphenous reflux; superficial-vein thrombosis; treatment.
© The Author(s) 2014 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalsPermissions.nav.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adjunctive techniques to minimize thrombotic complications following microfoam sclerotherapy of saphenous trunks and tributaries.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2021 Jul;9(4):904-909. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.11.015. Epub 2020 Nov 26. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2021. PMID: 33248297
-
Endovenous ablation with concomitant phlebectomy is a safe and effective method of treatment for symptomatic patients with axial reflux and large incompetent tributaries.J Vasc Surg. 2013 Jul;58(1):166-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2012.12.054. Epub 2013 Apr 6. J Vasc Surg. 2013. PMID: 23571079
-
Endovenous microfoam ablation of below knee superficial truncal veins is safe and effective in patients with prior saphenous treatment across a wide range of CEAP classes.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2022 Mar;10(2):390-394. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2021.08.015. Epub 2021 Aug 30. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2022. PMID: 34474174
-
Systematic review on the incidence and management of endovenous heat-induced thrombosis following endovenous thermal ablation of the great saphenous vein.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2021 Sep;9(5):1312-1320.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Feb 19. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2021. PMID: 33618065
-
Which endovenous ablation method does offer a better long-term technical success in the treatment of the incompetent great saphenous vein? Review.Vascular. 2016 Dec;24(6):649-657. doi: 10.1177/1708538116648035. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Vascular. 2016. PMID: 27126643 Review.
Cited by
-
Endovenous Laser Ablation for Treatment of a Partially Thrombosed Proximal Great Saphenous Vein.Case Rep Vasc Med. 2019 Jun 12;2019:1726978. doi: 10.1155/2019/1726978. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Vasc Med. 2019. PMID: 31285933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Decousus H, Quere I, Presles E, et al. Superficial venous thromboembolism: a large prospective epidemiologic study. Ann Int Med 2010; 152: 218–239. - PubMed
-
- Chengelis DL, Bendick PJ, Glover JL, et al. Progression of superficial venous thrombosis to deep vein thrombosis. J Vasc Surg 1996; 24: 745–749. - PubMed
-
- Verlato F, Zucchetta P, Prandoni P, et al. An unexpectedly high rate of pulmonary embolism in patients with superficial thrombophlebitis of the thigh. J Vasc Surg 1999; 30: 1113–1115. - PubMed
-
- Gillet JL, Perrin M, Cayman R. Superficial venous thrombosis of the lower limbs: prospective analysis in 100 patients [in French]. J Mal Vasc 2001; 26: 16–22. - PubMed
-
- Di Nisio M, Wichers IM, Middeldorp S. Treatment for superficial thrombophlebitis of the leg. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012; 3: CD004982–CD004982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

