Prognostic implication of HSPA (HSP70) in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant anthracycline-based chemotherapy
- PMID: 24307543
- PMCID: PMC4041939
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-013-0475-2
Prognostic implication of HSPA (HSP70) in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant anthracycline-based chemotherapy
Abstract
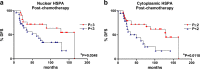
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is used in patients with locally advanced breast cancer to reduce tumor size before surgery. Unfortunately, resistance to chemotherapy may arise from a variety of mechanisms. Heat shock proteins (HSPs), which are highly expressed in mammary tumor cells, have been implicated in anticancer drug resistance. In spite of the widely described value of HSPs as molecular markers in cancer, their implications in breast tumors treated with anthracycline-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy has been poorly explored. In this study, we have evaluated, by immunohistochemistry, the expression of HSP27 (HSPB1) and HSP70 (HSPA) in serial biopsies from locally advanced breast cancer patients (n = 60) treated with doxorubicin (DOX)- or epirubicin (EPI)-based monochemotherapy. Serial biopsies were taken at days 1, 3, 7, and 21, and compared with prechemotherapy and surgical biopsies. After surgery, the patients received additional chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil. High nuclear HSPB1 and HSPA expressions were found in invasive cells after DOX/EPI administration (P < 0.001), but the drug did not affect the cytoplasmic expression of the HSPs. Infiltrating lymphocytes showed high nuclear HSPA (P < 0.01) levels at postchemotherapy. No correlations were found between HSPs expression and the clinical and pathological response to neoadjuvant therapy. However, in postchemotherapy biopsies, high nuclear (>31 % of the cells) and cytoplasmic HSPA expressions (>11 % of the tumor cells) were associated with better DFS (P = 0.0348 and P = 0.0118, respectively). We conclude that HSPA expression may be a useful prognostic marker in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant DOX/EPI chemotherapy indicating the need to change the administered drugs after surgery for overcoming drug resistance.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Heat shock protein expression and drug resistance in breast cancer patients treated with induction chemotherapy.Int J Cancer. 1998 Oct 23;79(5):468-75. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19981023)79:5<468::aid-ijc4>3.0.co;2-z. Int J Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9761114
-
Prognostic value of Bcl-2 in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant anthracycline based chemotherapy.Mol Oncol. 2008 Jun;2(1):102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2008.01.004. Epub 2008 Jan 13. Mol Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19383332 Free PMC article.
-
SerpinB3, a new prognostic tool in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Apr;132(3):807-18. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1625-9. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21695460
-
Sequencing of anthracyclines and taxanes in neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for early breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 18;2(2):CD012873. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012873.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30776132 Free PMC article.
-
Epirubicin: is it like doxorubicin in breast cancer? A clinical review.Breast. 2012 Apr;21(2):142-9. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2011.12.012. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Breast. 2012. PMID: 22260846 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytosolic Hsp70 as a biomarker to predict clinical outcome in patients with glioblastoma.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 20;14(8):e0221502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221502. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31430337 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and expression analysis of a heat-shock protein 70 gene in Polycelis sp.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015 Nov;20(6):907-15. doi: 10.1007/s12192-015-0608-x. Epub 2015 Aug 27. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015. PMID: 26311284 Free PMC article.
-
HSP70/IL-2 Treated NK Cells Effectively Cross the Blood Brain Barrier and Target Tumor Cells in a Rat Model of Induced Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 25;21(7):2263. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072263. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32218162 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Investigation to Identify Anticancer Targets of Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom in Human Hepatocarcinoma HepG2 Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2018 May 10;10(5):194. doi: 10.3390/toxins10050194. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29748501 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway Suppresses Proliferation of Burkitt's Lymphoma Raji Cells via Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, and Oxidative Stress by Modulating HSP70.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Sep 8;24:6255-6263. doi: 10.12659/MSM.910170. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30194286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A, Obeid M, Ortiz C, Criollo A, Mignot G, Maiuri MC, Ullrich E, Saulnier P, Yang H, Amigorena S, Ryffel B, Barrat FJ, Saftig P, Levi F, Lidereau R, Nogues C, Mira JP, Chompret A, Joulin V, Clavel-Chapelon F, Bourhis J, André F, Delaloge S, Tursz T, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat Med. 2007;13:1050–1059. doi: 10.1038/nm1622. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A, Obeid M, Mignot G, Ullrich E, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L. Cancer is not just a disease of a tissue: it is a host disease. How to reactivate host defense against tumors using conventional therapies of cancer? Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 2008;69:151–152. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2008.02.016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

