TIGRA: a targeted iterative graph routing assembler for breakpoint assembly
- PMID: 24307552
- PMCID: PMC3912421
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.162883.113
TIGRA: a targeted iterative graph routing assembler for breakpoint assembly
Abstract
Recent progress in next-generation sequencing has greatly facilitated our study of genomic structural variation. Unlike single nucleotide variants and small indels, many structural variants have not been completely characterized at nucleotide resolution. Deriving the complete sequences underlying such breakpoints is crucial for not only accurate discovery, but also for the functional characterization of altered alleles. However, our current ability to determine such breakpoint sequences is limited because of challenges in aligning and assembling short reads. To address this issue, we developed a targeted iterative graph routing assembler, TIGRA, which implements a set of novel data analysis routines to achieve effective breakpoint assembly from next-generation sequencing data. In our assessment using data from the 1000 Genomes Project, TIGRA was able to accurately assemble the majority of deletion and mobile element insertion breakpoints, with a substantively better success rate and accuracy than other algorithms. TIGRA has been applied in the 1000 Genomes Project and other projects and is freely available for academic use.
Figures
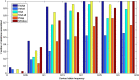
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
