CD13 regulates anchorage and differentiation of the skeletal muscle satellite stem cell population in ischemic injury
- PMID: 24307555
- PMCID: PMC4037355
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1610
CD13 regulates anchorage and differentiation of the skeletal muscle satellite stem cell population in ischemic injury
Abstract
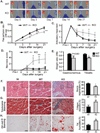
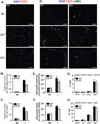
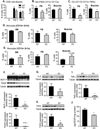
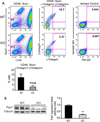
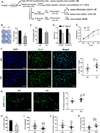
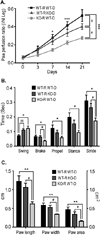
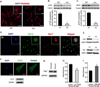
CD13 is a multifunctional cell surface molecule that regulates inflammatory and angiogenic mechanisms in vitro, but its contribution to these processes in vivo or potential roles in stem cell biology remains unexplored. We investigated the impact of loss of CD13 on a model of ischemic skeletal muscle injury that involves angiogenesis, inflammation, and stem cell mobilization. Consistent with its role as an inflammatory adhesion molecule, lack of CD13 altered myeloid trafficking in the injured muscle, resulting in cytokine profiles skewed toward a prohealing environment. Despite this healing-favorable context, CD13(KO) animals showed significantly impaired limb perfusion with increased necrosis, fibrosis, and lipid accumulation. Capillary density was correspondingly decreased, implicating CD13 in skeletal muscle angiogenesis. The number of CD45-/Sca1-/α7-integrin+/β1-integrin+ satellite cells was markedly diminished in injured CD13(KO) muscles and adhesion of isolated CD13(KO) satellite cells was impaired while their differentiation was accelerated. Bone marrow transplantation studies showed contributions from both host and donor cells to wound healing. Importantly, CD13 was coexpressed with Pax7 on isolated muscle-resident satellite cells. Finally, phosphorylated-focal adhesion kinase and ERK levels were reduced in injured CD13(KO) muscles, consistent with CD13 regulating satellite cell adhesion, potentially contributing to the maintenance and renewal of the satellite stem cell pool and facilitating skeletal muscle regeneration.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; CD13; Hind limb ischemia; Muscle stem cells.
© 2013 AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic deletion of TNFR2 augments inflammatory response and blunts satellite-cell-mediated recovery response in a hind limb ischemia model.FASEB J. 2015 Apr;29(4):1208-19. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-249813. Epub 2014 Dec 2. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25466901 Free PMC article.
-
Satellite cell-specific ablation of Cdon impairs integrin activation, FGF signalling, and muscle regeneration.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020 Aug;11(4):1089-1103. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12563. Epub 2020 Feb 27. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020. PMID: 32103583 Free PMC article.
-
Myoblast-conditioned media improve regeneration and revascularization of ischemic muscles in diabetic mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Apr 12;6(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0063-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25889676 Free PMC article.
-
Functional dysregulation of stem cells during aging: a focus on skeletal muscle stem cells.FEBS J. 2013 Sep;280(17):4051-62. doi: 10.1111/febs.12221. Epub 2013 Mar 21. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23452120 Review.
-
Systematic Interrogation of Angiogenesis in the Ischemic Mouse Hind Limb: Vulnerabilities and Quality Assurance.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Oct;40(10):2454-2467. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315028. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32787524 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
α7nAChR is expressed in satellite cells at different myogenic status during skeletal muscle wound healing in rats.J Mol Histol. 2015 Dec;46(6):499-509. doi: 10.1007/s10735-015-9641-4. J Mol Histol. 2015. PMID: 26498641
-
Silicon-Gold Nanoparticles Affect Wharton's Jelly Phenotype and Secretome during Tri-Lineage Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 15;23(4):2134. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042134. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216249 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenic and Arthritogenic Properties of the Soluble Form of CD13.J Immunol. 2019 Jul 15;203(2):360-369. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801276. Epub 2019 Jun 12. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31189572 Free PMC article.
-
Human Embryonic-Derived Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells (hES-MP Cells) are Fully Supported in Culture with Human Platelet Lysates.Bioengineering (Basel). 2020 Jul 20;7(3):75. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering7030075. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32698321 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of skeletal myogenesis in C2C12 cells through modulation of Pax7, MyoD, and myogenin via different low-frequency electromagnetic field energies.Technol Health Care. 2022;30(S1):371-382. doi: 10.3233/THC-THC228034. Technol Health Care. 2022. PMID: 35124612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muller WA. Sorting the Signals from the Signals in the Noisy Environment of Inflammation. Sci Signal. 2011;4:pe23. - PubMed
-
- McGettrick HM, Butler LM, Buckley CD, et al. Tissue stroma as a regulator of leukocyte recruitment in inflammation. Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 2012;91:385–400. - PubMed
-
- Auffray C, Fogg D, Garfa M, et al. Monitoring of Blood Vessels and Tissues by a Population of Monocytes with Patrolling Behavior. Science. 2007;317:666–670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

