Interactions between herpesvirus entry mediator (TNFRSF14) and latency-associated transcript during herpes simplex virus 1 latency
- PMID: 24307582
- PMCID: PMC3911542
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02467-13
Interactions between herpesvirus entry mediator (TNFRSF14) and latency-associated transcript during herpes simplex virus 1 latency
Abstract
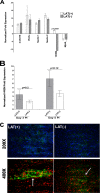
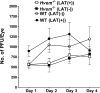
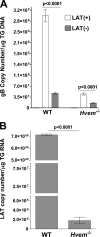
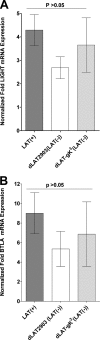
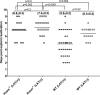
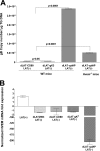
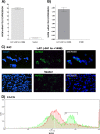
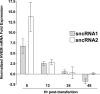
Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) is one of several cell surface proteins herpes simplex virus (HSV) uses for attachment/entry. HVEM regulates cellular immune responses and can also increase cell survival. Interestingly, latency-associated transcript (LAT), the only viral gene consistently expressed during neuronal latency, enhances latency and reactivation by promoting cell survival and by helping the virus evade the host immune response. However, the mechanisms of these LAT activities are not well understood. We show here for the first time that one mechanism by which LAT enhances latency and reactivation appears to be by upregulating HVEM expression. HSV-1 latency/reactivation was significantly reduced in Hvem(-/-) mice, indicating that HVEM plays a significant role in HSV-1 latency/reactivation. Furthermore, LAT upregulated HVEM expression during latency in vivo and also when expressed in vitro in the absence of other viral factors. This study suggests a mechanism whereby LAT upregulates HVEM expression potentially through binding of two LAT small noncoding RNAs to the HVEM promoter and that the increased HVEM then leads to downregulation of immune responses in the latent microenvironment and increased survival of latently infected cells. Thus, one of the mechanisms by which LAT enhances latency/reactivation appears to be through increasing expression of HVEM.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI89553/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013191/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- AI093941/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- EY15557/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067890/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- EY13615/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI048073/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI033068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI089553/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014966/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI093941/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1P20RR15635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- EY14966/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R37AI033068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013615/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015557/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

