Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in adults: a shared position statement of the Italian Association for the Study of the Pancreas
- PMID: 24307787
- PMCID: PMC3848141
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.7930
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in adults: a shared position statement of the Italian Association for the Study of the Pancreas
Abstract
This is a medical position statement developed by the Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency collaborative group which is a part of the Italian Association for the Study of the Pancreas (AISP). We covered the main diseases associated with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) which are of common interest to internists/gastroenterologists, oncologists and surgeons, fully aware that EPI may also occur together with many other diseases, but less frequently. A preliminary manuscript based on an extended literature search (Medline/PubMed, Cochrane Library and Google Scholar) of published reports was prepared, and key recommendations were proposed. The evidence was discussed at a dedicated meeting in Bologna during the National Meeting of the Association in October 2012. Each of the proposed recommendations and algorithms was discussed and an initial consensus was reached. The final draft of the manuscript was then sent to the AISP Council for approval and/or modification. All concerned parties approved the final version of the manuscript in June 2013.
Keywords: Chronic pancreatitis; Clinical studies; Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency; Gastric surgery; Pancreatic neoplasms; Pancreatic surgery; Risk factors.
Figures



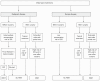

References
-
- Gullo L, Pezzilli R, Priori P, Baldoni F, Paparo F, Mattioli G. Pure pancreatic juice collection over 24 consecutive hours. Pancreas. 1987;2:620–623. - PubMed
-
- Scheele G, Bartelt D, Bieger W. Characterization of human exocrine pancreatic proteins by two-dimensional isoelectric focusing/sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. Gastroenterology. 1981;80:461–473. - PubMed
-
- Layer P, Go VL, DiMagno EP. Fate of pancreatic enzymes during small intestinal aboral transit in humans. Am J Physiol. 1986;251:G475–G480. - PubMed
-
- Granger M, Abadie B, Marchis-Mouren G. Limited action of trypsin on porcine pancreatic amylase: characterization of the fragments. FEBS Lett. 1975;56:189–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

