Low Molecular Weight Heparin Induced Skin Necrosis without Platelet Fall Revealing Immunoallergic Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 24307958
- PMCID: PMC3835902
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/849168
Low Molecular Weight Heparin Induced Skin Necrosis without Platelet Fall Revealing Immunoallergic Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia
Abstract
Low molecular weight heparins (LMWH) are commonly used in the ICU setting for thromboprophylaxis as well as curative decoagulation as required during renal replacement therapy (RRT). A rare adverse event revealing immunoallergic LMWH induced thrombopenia (HIT) is skin necrosis at injection sites. We report the case of a patient presenting with skin necrosis witnessing an HIT after RRT, without thrombocytopenia. The mechanism remains unclear. Anti-PF4/heparin antibodies, functional tests (HIPA and/or SRA), and skin biopsy are of great help to evaluate differential diagnosis with a low pretest probability 4T's score.
Figures
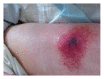
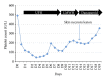
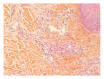
References
-
- Warkentin TE, Linkins L-A. Non-necrotizing heparin-induced skin lesions and the 4T’s score. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2010;8(7):1483–1485. - PubMed
-
- Schindewolf M, Kroll H, Ackermann H, et al. Heparin-induced non-necrotizing skin lesions: rarely associated with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2010;8(7):1486–1491. - PubMed
-
- Wütschert R, Piletta P, Bounameaux H. Adverse skin reactions to low molecular weight heparins: frequency, management and prevention. Drug Safety. 1999;20(6):515–525. - PubMed
-
- Lo GK, Juhl D, Warkentin TE, Sigouin CS, Eichler P, Greinacher A. Evaluation of pretest clinical score (4 T’s) for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in two clinical settings. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2006;4(4):759–765. - PubMed
-
- Harenberg J, Huhle G, Wang L, Hoffmann U, Bayerl C, Kerowgan M. Association of heparin-induced skin lesions, intracutaneous tests, and heparin-induced IgG. Allergy. 1999;54(5):473–477. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

