Rapid identification of aldose reductase inhibitory compounds from Perilla frutescens
- PMID: 24308003
- PMCID: PMC3838804
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/679463
Rapid identification of aldose reductase inhibitory compounds from Perilla frutescens
Abstract
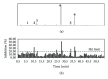
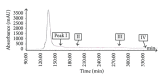
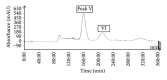
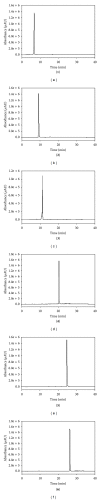
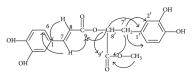
The ethyl acetate (EtOAc) soluble fraction of methanol extracts of Perilla frutescens (P. frutescens) inhibits aldose reductase (AR), the key enzyme in the polyol pathway. Our investigation of inhibitory compounds from the EtOAc soluble fraction of P. frutescens was followed by identification of the inhibitory compounds by a combination of HPLC microfractionation and a 96-well enzyme assay. This allowed the biological activities to be efficiently matched with selected HPLC peaks. Structural analyses of the active compounds were performed by LC-MS(n). The main AR inhibiting compounds were tentatively identified as chlorogenic acid and rosmarinic acid by LC-MS(n). A two-step high speed counter current chromatography (HSCCC) isolation method was developed with a solvent system of n-hexane-ethyl acetate-methanol-water at 1.5:5:1:5, v/v and 3:7:5:5, v/v. The chemical structures of the isolated compounds were determined by (1)H- and (13)C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry (NMR). The main compounds inhibiting AR in the EtOAc fraction of methanol extracts of P. frutescens were identified as chlorogenic acid (2) (IC50 = 3.16 μ M), rosmarinic acid (4) (IC50 = 2.77 μ M), luteolin (5) (IC50 = 6.34 μ M), and methyl rosmarinic acid (6) (IC50 = 4.03 μ M).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perilla frutescens: A Rich Source of Pharmacological Active Compounds.Molecules. 2022 Jun 2;27(11):3578. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113578. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and identification of phenolic compounds from the seeds of Perilla frutescens (L.) and their inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase and aldose reductase.Food Chem. 2012 Dec 1;135(3):1397-403. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.05.104. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22953872
-
Preparative isolation of aldose reductase inhibitory compounds from Nardostachys chinensis by elution-extrusion counter-current chromatography.Arch Pharm Res. 2014 Oct;37(10):1271-9. doi: 10.1007/s12272-014-0328-2. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Arch Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24424606
-
Structural characterisation and antioxidant activity evaluation of phenolic compounds from cold-pressed Perilla frutescens var. arguta seed flour.Food Chem. 2014 Dec 1;164:150-7. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.062. Epub 2014 May 20. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24996318
-
The Role and Mechanism of Perilla frutescens in Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2023 Aug 4;28(15):5883. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155883. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Review of Perilla frutescens: Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Mechanisms, and Industrial Applications in Food and Health Products.Foods. 2025 Apr 3;14(7):1252. doi: 10.3390/foods14071252. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purple perilla extracts with α-asarone enhance cholesterol efflux from oxidized LDL-exposed macrophages.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Apr;35(4):957-65. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2101. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25673178 Free PMC article.
-
Perilla frutescens: A Rich Source of Pharmacological Active Compounds.Molecules. 2022 Jun 2;27(11):3578. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113578. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Aldose Reductase, Protein Glycation, and Antioxidant Inhibitory Activities of Bioactive Flavonoids in Matricaria recutita L. and Their Structure-Activity Relationship.J Diabetes Res. 2018 Apr 10;2018:3276162. doi: 10.1155/2018/3276162. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 29850602 Free PMC article.
-
Cataract Preventive Role of Isolated Phytoconstituents: Findings from a Decade of Research.Nutrients. 2018 Oct 26;10(11):1580. doi: 10.3390/nu10111580. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30373159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001;414(6865):813–820. - PubMed
-
- Oates PJ, Mylari BL. Aldose reductase inhibitors: therapeutic implications for diabetic complications. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 1999;8(12):2095–2119. - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson DR, Stevens EJ, Diemel LT. Aldose reductase inhibitors and their potential for the treatment of diabetic complications. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 1994;15(8):293–297. - PubMed
-
- Engerman RL, Kern TS. Aldose reductase inhibition fails to prevent retinopathy in diabetic and galactosemic dogs. Diabetes. 1993;42(6):820–825. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar A, Srivastava SK. Aldose reductase: congenial and injurious profiles of an enigmatic enzyme. Biochemical Medicine and Metabolic Biology. 1992;48(2):91–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

