Sustained effectiveness of 10 kHz high-frequency spinal cord stimulation for patients with chronic, low back pain: 24-month results of a prospective multicenter study
- PMID: 24308759
- PMCID: PMC4282782
- DOI: 10.1111/pme.12294
Sustained effectiveness of 10 kHz high-frequency spinal cord stimulation for patients with chronic, low back pain: 24-month results of a prospective multicenter study
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the long-term efficacy and safety of paresthesia-free high-frequency spinal cord stimulation (HF10 SCS) for the treatment of chronic, intractable pain of the low back and legs.
Design: Prospective, multicenter, observational study.
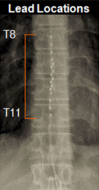
Method: Patients with significant chronic low back pain underwent implantation of a spinal cord stimulator capable of HF10 SCS. Patients' pain ratings, disability, sleep disturbances, opioid use, satisfaction, and adverse events were assessed for 24 months.
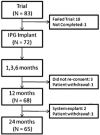
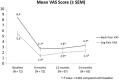
Results: After a trial period, 88% (72 of 82) of patients reported a significant improvement in pain scores and underwent the permanent implantation of the system. Ninety percent (65 of 72) of patients attended a 24-month follow-up visit. Mean back pain was reduced from 8.4 ± 0.1 at baseline to 3.3 ± 0.3 at 24 months (P < 0.001), and mean leg pain from 5.4 ± 0.4 to 2.3 ± 0.3 (P < 0.001). Concomitantly to the pain relief, there were significant decreases in opioid use, Oswestry Disability Index score, and sleep disturbances. Patients' satisfaction and recommendation ratings were high. Adverse Events were similar in type and frequency to those observed with traditional SCS systems.
Conclusions: In patients with chronic low back pain, HF10 SCS resulted in clinically significant and sustained back and leg pain relief, functional and sleep improvements, opioid use reduction, and high patient satisfaction. These results support the long-term safety and sustained efficacy of HF10 SCS.
Keywords: Chronic Low Back Pain; Failed Back Surgery Syndrome; High-Frequency Stimulation; Spinal Cord Stimulation.
© 2013 The Authors. Pain Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

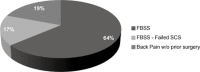
References
-
- Van Buyten JP, Linderoth B. “The failed back surgery syndrome”: Definition and therapeutic algorithms: An update. Eur J Pain Suppl. 2010;4:273–286.
-
- Wilkinson HA. The Failed Back Syndrome: Etiology and Therapy. Philadelphia, PA: Harper & Row; 1991.
-
- Chou R, Baisden J, Carragee EJ. Surgery for low back pain: A review of the evidence for an American Pain Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Spine. 2009;34:1094–1109. - PubMed
-
- North RB, Kidd DH, Farrokhi F, Piantadosi SA. Spinal cord stimulation versus repeated lumbosacral spine surgery for chronic pain: A randomized, controlled trial. Neurosurgery. 2005;56:98–106. - PubMed
-
- Kumar K, Taylor RS, Jacques L. The effects of spinal cord stimulation in neuropathic pain are sustained: A 24-month follow-up of the prospective randomized controlled multicenter trial of the effectiveness spinal cord stimulation. Neurosurgery. 2008;63:762–770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

