Plan selection in Medicare Part D: evidence from administrative data
- PMID: 24308882
- PMCID: PMC4513642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhealeco.2013.06.006
Plan selection in Medicare Part D: evidence from administrative data
Abstract
We study the Medicare Part D prescription drug insurance program as a bellwether for designs of private, non-mandatory health insurance markets, focusing on the ability of consumers to evaluate and optimize their choices of plans. Our analysis of administrative data on medical claims in Medicare Part D suggests that fewer than 25% of individuals enroll in plans that are ex ante as good as the least cost plan specified by the Plan Finder tool made available to seniors by the Medicare administration, and that consumers on average have expected excess spending of about $300 per year, or about 15% of expected total out-of-pocket cost for drugs and Part D insurance. These numbers are hard to reconcile with decision costs alone; it appears that unless a sizeable fraction of consumers place large values on plan features other than cost, they are not optimizing effectively.
Keywords: Administrative data; C25; D12; H51; Health insurance demand; I11; I18; Insurance claims data; Medicare; Prescription drugs.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures






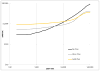
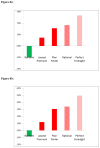
References
-
- Agarwal S, Driscoll JC, Gabaix X, Laibson D. The age of reason: Financial decisions over the life cycle and implications of regulation. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity. 2009 Fall;:51–101.
-
- Aron-Dine A, Einav L, Finkelstein A, Cullen MR. Working Paper No. 17802. National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER); 2012. Moral Hazard in Health Insurance: How Important Is Forward Looking Behavior?
-
- Bach PB, McClellan MB. A prescription of a modern Medicare program. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;353:2733–2735. - PubMed
-
- Bach PB, McClellan MB. The first months of the prescription-drug benefit: A CMS update. New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;354:2312–2314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

