Dopamine D3 receptor inhibits the ubiquitin-specific peptidase 48 to promote NHE3 degradation
- PMID: 24308971
- PMCID: PMC3929671
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.13-243840
Dopamine D3 receptor inhibits the ubiquitin-specific peptidase 48 to promote NHE3 degradation
Abstract
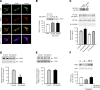
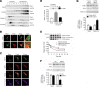
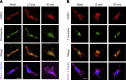
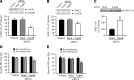
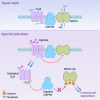
The dopamine D3 receptor (D3R) is crucial in the regulation of blood pressure and sodium balance, in that Drd3 gene ablation in mice results in hypertension and failure to excrete a dietary salt load. The mechanism responsible for the renal sodium retention in these mice is largely unknown. We now offer and describe a novel mechanism by which D3R decreases sodium transport in the long term by inhibiting the deubiquitinylating activity of ubiquitin-specific peptidase 48 (USP48), thereby promoting Na(+)-H(+) exchanger (NHE)-3 degradation. We found that stimulation with the D3R-specific agonist PD128907 (1 μM, 30 min) promoted the interaction and colocalization among D3R, NHE3, and USP48; inhibited USP48 activity (-35±6%, vs. vehicle), resulting in increased ubiquitinylated NHE3 (+140±10%); and decreased NHE3 expression (-50±9%) in human renal proximal tubule cells (hRPTCs). USP48 silencing decreased NHE3's half-life (USP48 siRNA t1/2=6.1 h vs. vehicle t1/2=12.9 h), whereas overexpression of USP48 increased NHE3 half-life (t1/2=21.8 h), indicating that USP48 protects NHE3 from degradation via deubiquitinylation. USP48 accounted for ∼30% of the total deubiquitinylating activity in these cells. Extending our studies in vivo, we found that pharmacologic blockade of D3R via the D3R-specific antagonist GR103691 (1 μg/kg/min, 4 d) in C57Bl/6J mice increased renal NHE3 expression (+310±15%, vs. vehicle), whereas an innovative kidney-restricted Usp48 silencing via siRNA (3 μg/d, 7 d) increased ubiquitinylated NHE3 (+250±30%, vs. controls), decreased total NHE3 (-23±2%), and lowered blood pressure (-24±2 mm Hg), compared with that in control mice that received either the vehicle or nonsilencing siRNA. Our data demonstrate a crucial role for the dynamic interaction between D3R and USP48 in the regulation of NHE3 expression and function.
Keywords: C57Bl/6 mice; blood pressure; kidney; renal proximal tubule cells.
Figures



References
-
- Felder R. A., Seikaly M. G., Cody P., Eisner G. M., Jose P. A. (1990) Attenuated renal response to dopaminergic drugs in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 15, 560–569 - PubMed
-
- Chen C. J., Lokhandwala M. F. (1992) An impairment of renal tubular DA-1 receptor function as the causative factor for diminished natriuresis to volume expansion in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. A. 14, 615–628 - PubMed
-
- Luippold G., Küster E., Joos T. O., Mühlbauer B. (1998) Dopamine D3 receptor activation modulates renal function in anesthetized rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 358, 690–693 - PubMed
-
- Ladines C. A., Zeng C., Asico L. D., Sun X., Pocchiari F., Semeraro C., Pisegna J., Wank S., Yamaguchi I., Eisner G. M., Jose P. A. (2001) Impaired renal D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptor interaction in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 281, R1071–R1078 - PubMed
-
- Sibley D. R. (1999) New insights into dopaminergic receptor function using antisense and genetically altered animals. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 39, 313–314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK039308/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL068686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL023081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK090918/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090918/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL023081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092196/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL092196/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37HL023081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL068686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK039308/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL074940/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL074940/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

