The kidney as a reservoir for HIV-1 after renal transplantation
- PMID: 24309185
- PMCID: PMC3904571
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013050564
The kidney as a reservoir for HIV-1 after renal transplantation
Abstract
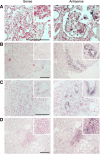
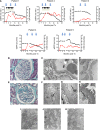
Since the recent publication of data showing favorable outcomes for patients with HIV-1 and ESRD, kidney transplantation has become a therapeutic option in this population. However, reports have documented unexplained reduced allograft survival in these patients. We hypothesized that the unrecognized infection of the transplanted kidney by HIV-1 can compromise long-term allograft function. Using electron microscopy and molecular biology, we examined protocol renal transplant biopsies from 19 recipients with HIV-1 who did not have detectable levels of plasma HIV-1 RNA at transplantation. We found that HIV-1 infected the kidney allograft in 68% of these patients. Notably, HIV-1 infection was detected in either podocytes predominately (38% of recipients) or tubular cells only (62% of recipients). Podocyte infection associated with podocyte apoptosis and loss of differentiation markers as well as a faster decline in allograft function compared with tubular cell infection. In allografts with tubular cell infection, epithelial cells of the proximal convoluted tubules frequently contained abnormal mitochondria, and both patients who developed features of subclinical acute cellular rejection had allografts with tubular cell infection. Finally, we provide a novel noninvasive test for determining HIV-1 infection of the kidney allograft by measuring HIV-1 DNA and RNA levels in patients' urine. In conclusion, HIV-1 can infect kidney allografts after transplantation despite undetectable viremia, and this infection might influence graft outcome.
Figures

Comment in
-
Kidney infection with HIV-1 following kidney transplantation.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Feb;25(2):212-5. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013101112. Epub 2013 Dec 5. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24309191 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adih WK, Selik RM, Hu X: Trends in diseases reported on US death certificates that mentioned HIV infection, 1996-2006. J Int Assoc Physicians AIDS Care (Chic) 10: 5–11, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Wyatt CM, Meliambro K, Klotman PE: Recent progress in HIV-associated nephropathy. Annu Rev Med 63: 147–159, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Marras D, Bruggeman LA, Gao F, Tanji N, Mansukhani MM, Cara A, Ross MD, Gusella GL, Benson G, D’Agati VD, Hahn BH, Klotman ME, Klotman PE: Replication and compartmentalization of HIV-1 in kidney epithelium of patients with HIV-associated nephropathy. Nat Med 8: 522–526, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Stock PG, Barin B, Murphy B, Hanto D, Diego JM, Light J, Davis C, Blumberg E, Simon D, Subramanian A, Millis JM, Lyon GM, Brayman K, Slakey D, Shapiro R, Melancon J, Jacobson JM, Stosor V, Olson JL, Stablein DM, Roland ME: Outcomes of kidney transplantation in HIV-infected recipients. N Engl J Med 363: 2004–2014, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

