Targeting plasticity with vagus nerve stimulation to treat neurological disease
- PMID: 24309259
- PMCID: PMC4615598
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63327-9.00010-2
Targeting plasticity with vagus nerve stimulation to treat neurological disease
Abstract
Pathological neural activity in a variety of neurological disorders could be treated by directing plasticity to specifically renormalize aberrant neural circuits, thereby restoring normal function. Brief bursts of acetylcholine and norepinephrine can enhance the neural plasticity associated with coincident events. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) represents a safe and effective means to trigger the release of these neuromodulators with a high degree of temporal control. VNS-event pairing can generate highly specific and long-lasting plasticity in sensory and motor cortex. Based on the capacity to drive specific changes in neural circuitry, VNS paired with experience has been successful in effectively ameliorating animal models of chronic tinnitus, stroke, and posttraumatic stress disorder. Targeted plasticity therapy utilizing VNS is currently being translated to humans to treat chronic tinnitus and improve motor recovery after stroke. This chapter will discuss the current progress of VNS paired with experience to drive specific plasticity to treat these neurological disorders and will evaluate additional future applications of targeted plasticity therapy.
Keywords: acetylcholine; cortical plasticity; neuromodulators; norepinephrine; recovery; targeted plasticity; vagus nerve stimulation (VNS).
© 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M. P. K. is a consultant for and has a financial interest in MicroTransponder, Inc.
Figures
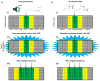
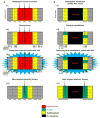

References
-
- Anlezark G, Crow T, Greenway A. Impaired learning and decreased cortical norepinephrine after bilateral locus coeruleus lesions. Science. 1973;181:682–684. - PubMed
-
- Arns M, De Ridder D. Neurofeedback 2.0? J Neurother. 2011;15:91–93.
-
- Avital A, Goshen I, Kamsler A, Segal M, Iverfeldt K, Richter-Levin G, Yirmiya R. Impaired interleukin-1 signaling is associated with deficits in hippocampal memory processes and neural plasticity. Hippocampus. 2003;13:826–834. - PubMed
-
- Axelson HW, Winkler T, Flygt J, Djupsjö A, Hånell A, Marklund N. Plasticity of the contralateral motor cortex following focal traumatic brain injury in the rat. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2013;31:73–85. - PubMed
-
- Baskerville K, Schweitzer J, Herron P. Effects of cholinergic depletion on experience-dependent plasticity in the cortex of the rat. Neuroscience. 1997;80:1159–1169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

