Decoding speech for understanding and treating aphasia
- PMID: 24309265
- PMCID: PMC4043958
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63327-9.00018-7
Decoding speech for understanding and treating aphasia
Abstract
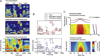
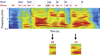
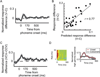
Aphasia is an acquired language disorder with a diverse set of symptoms that can affect virtually any linguistic modality across both the comprehension and production of spoken language. Partial recovery of language function after injury is common but typically incomplete. Rehabilitation strategies focus on behavioral training to induce plasticity in underlying neural circuits to maximize linguistic recovery. Understanding the different neural circuits underlying diverse language functions is a key to developing more effective treatment strategies. This chapter discusses a systems identification analytic approach to the study of linguistic neural representation. The focus of this framework is a quantitative, model-based characterization of speech and language neural representations that can be used to decode, or predict, speech representations from measured brain activity. Recent results of this approach are discussed in the context of applications to understanding the neural basis of aphasia symptoms and the potential to optimize plasticity during the rehabilitation process.
Keywords: aphasia; decoding; language; neural encoding; speech.
© 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intensive language training enhances brain plasticity in chronic aphasia.BMC Biol. 2004 Aug 25;2:20. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-2-20. BMC Biol. 2004. PMID: 15331014 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Language features in the acute phase of poststroke severe aphasia could predict the outcome.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017 Apr;53(2):249-255. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.16.04255-6. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017. PMID: 27412072
-
Acquired focal brain lesions in childhood: effects on development and reorganization of language.Brain Lang. 2008 Sep;106(3):211-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2007.12.010. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Brain Lang. 2008. PMID: 18267339
-
Impairments of speech production and speech perception in aphasia.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994 Oct 29;346(1315):29-36. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0125. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994. PMID: 7886150 Review.
-
Interdisciplinary approaches to understanding the inner speech, with emphasis on the role of incorporating clinical data.Eur J Neurosci. 2024 Sep;60(5):4785-4797. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16470. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Eur J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39015943 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal lobe networks supporting the comprehension of spoken words.Brain. 2017 Sep 1;140(9):2370-2380. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx169. Brain. 2017. PMID: 29050387 Free PMC article.
-
The use of intracranial recordings to decode human language: Challenges and opportunities.Brain Lang. 2019 Jun;193:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2016.06.003. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Brain Lang. 2019. PMID: 27377299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Encoding and Decoding Models in Cognitive Electrophysiology.Front Syst Neurosci. 2017 Sep 26;11:61. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00061. eCollection 2017. Front Syst Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29018336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding Inner Speech Using Electrocorticography: Progress and Challenges Toward a Speech Prosthesis.Front Neurosci. 2018 Jun 21;12:422. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00422. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29977189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling Cognitive Interference: fNIRS Insights Into Poststroke Aphasia During Stroop Tasks.Neural Plast. 2025 Mar 31;2025:1456201. doi: 10.1155/np/1456201. eCollection 2025. Neural Plast. 2025. PMID: 40201621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelson EH, Bergen JR. Spatiotemporal energy models for the perception of motion. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 1985;2:284–299. - PubMed
-
- Aertsen AM, Johannesma PI. The spectro-temporal receptive field. A functional characteristic of auditory neurons. Biol. Cybern. 1981;42:133–143. - PubMed
-
- Bialek W, Rieke F, De Ruyter Van Steveninck RR, Warland D. Reading a neural code. Science. 1991;252:1854–1857. - PubMed
-
- Bouchard KE, Mesgarani N, Johnson K, Chang EF. Functional organization of human sensorimotor cortex for speech articulation. Nature. 2013;495(7441):327–332. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature11911. Epub 2013 Feb 20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Breiman L. Statistical Modeling: The Two Cultures. Stat. Sci. 2001;16:199–231.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

