Sickness behaviour after lipopolysaccharide treatment in ghrelin deficient mice
- PMID: 24309634
- PMCID: PMC3951816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2013.11.017
Sickness behaviour after lipopolysaccharide treatment in ghrelin deficient mice
Abstract
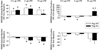
Ghrelin is an orexigenic hormone produced mainly by the gastrointestinal system and the brain. Much evidence also indicates a role for ghrelin in sleep and thermoregulation. Further, ghrelin was recently implicated in immune system modulation. Administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces fever, anorexia, and increased non-rapid-eye movement sleep (NREMS) and these actions are mediated primarily by proinflammatory cytokines. Ghrelin reduces LPS-induced fever, suppresses circulating levels of proinflammatory cytokines and reduces the severity and mortality of various models of experimental endotoxemia. In the present study, we determined the role of intact ghrelin signaling in LPS-induced sleep, feeding, and thermoregulatory responses in mice. Sleep-wake activity was determined after intraperitoneal, dark onset administration of 0.4, 2 and 10 μg LPS in preproghrelin knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice. In addition, body temperature, motor activity and changes in 24-h food intake and body weight were measured. LPS induced dose-dependent increases in NREMS, and suppressed rapid-eye movement sleep, electroencephalographic slow-wave activity, motor activity, food intake and body weight in both Ppg KO and WT mice. Body temperature changes showed a biphasic pattern with a decrease during the dark period followed by an increase in the light phase. The effects of the low and middle doses of LPS were indistinguishable between the two genotypes. Administration of 10 μg LPS, however, induced significantly larger changes in NREMS and wakefulness amounts, body temperature, food intake and body weight in the Ppg KO mice. These findings support a role for ghrelin as an endogenous modulator of inflammatory responses and a central component of arousal and feeding circuits.
Keywords: Body temperature; Electroencephalogram; Food intake; Ghrelin; Sleep.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diurnal variation of lipopolysaccharide-induced alterations in sleep and body temperature of interleukin-6-deficient mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2005 Jan;19(1):40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2004.04.001. Brain Behav Immun. 2005. PMID: 15581737
-
Restricted feeding-induced sleep, activity, and body temperature changes in normal and preproghrelin-deficient mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):R467-77. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00557.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19939974 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous sleep and homeostatic sleep regulation in ghrelin knockout mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Jul;293(1):R510-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00155.2007. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17409264
-
Central but not systemic administration of ghrelin induces wakefulness in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041172. Epub 2012 Jul 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22815958 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin as a Survival Hormone.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Dec;28(12):843-854. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29097101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microglia Are Necessary to Regulate Sleep after an Immune Challenge.Biology (Basel). 2022 Aug 19;11(8):1241. doi: 10.3390/biology11081241. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009868 Free PMC article.
-
Quiescence Enhances Survival during Viral Infection in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Neurosci. 2024 Aug 28;44(35):e1700222024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1700-22.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39060176 Free PMC article.
-
Hirsutanol A Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Expression and Cytokines Production and Improves Endotoxemia-Induced Acute Sickness Behavior and Acute Lung Injury.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jun 17;17(6):360. doi: 10.3390/md17060360. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31213027 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoteichoic acid, a cell wall component of Gram-positive bacteria, induces sleep and fever and suppresses feeding.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Feb;92:184-192. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.008. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33307170 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the pathogenesis of insomnia and acupuncture intervention strategies based on the microbiota-gut-brain axis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 19;15:1456848. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1456848. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39364160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander C, Rietschel ET. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides and innate immunity. J Endotoxin. Res. 2001;7:167–202. - PubMed
-
- Basa NR, Wang L, Arteaga JR, Heber D, Livingston EH, Tache Y. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide shifts fasted plasma ghrelin to postprandial levels in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2003;343:25–28. - PubMed
-
- Bodosi B, Gardi J, Hajdu I, Szentirmai E, Obal F, Jr, Krueger JM. Rhythms of ghrelin, leptin, and sleep in rats: effects of the normal diurnal cycle, restricted feeding, and sleep deprivation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004;287:R1071–R1079. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Zhao J, Yang J, Zhang Z, Du J, Tang C. Therapeutic effects of ghrelin on endotoxic shock in rats. Eur. J Pharmacol. 2003;473:171–176. - PubMed
-
- Chorny A, Anderson P, Gonzalez-Rey E, Delgado M. Ghrelin protects against experimental sepsis by inhibiting high-mobility group box 1 release and by killing bacteria. J Immunol. 2008;180:8369–8377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

