Hedgehog signaling controls T cell killing at the immunological synapse
- PMID: 24311692
- PMCID: PMC4022134
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1244689
Hedgehog signaling controls T cell killing at the immunological synapse
Abstract
The centrosome is essential for cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) function, contacting the plasma membrane and directing cytotoxic granules for secretion at the immunological synapse. Centrosome docking at the plasma membrane also occurs during cilia formation. The primary cilium, formed in nonhematopoietic cells, is essential for vertebrate Hedgehog (Hh) signaling. Lymphocytes do not form primary cilia, but we found and describe here that Hh signaling played an important role in CTL killing. T cell receptor activation, which "prearms" CTLs with cytotoxic granules, also initiated Hh signaling. Hh pathway activation occurred intracellularly and triggered Rac1 synthesis. These events "prearmed" CTLs for action by promoting the actin remodeling required for centrosome polarization and granule release. Thus, Hh signaling plays a role in CTL function, and the immunological synapse may represent a modified cilium.
Figures
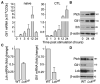
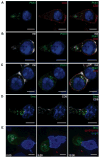


Comment in
-
Immunology. Do T cells have a cilium?Science. 2013 Dec 6;342(6163):1177-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1248078. Science. 2013. PMID: 24311670 No abstract available.
References
-
- Stinchcombe JC, Majorovits E, Bossi G, Fuller S, Griffiths GM. Nature. 2006;443:462–465. - PubMed
-
- Monks CR, Freiberg BA, Kupfer H, Sciaky N, Kupfer A. Nature. 1998;395:82–86. - PubMed
-
- Stinchcombe JC, Griffiths GM. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:495–517. - PubMed
-
- Wheatley DN. Pathobiology. 1995;63:222–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

