Prognostic factors associated with the response to sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24311955
- PMCID: PMC3851351
- DOI: 10.3747/co.20.1596
Prognostic factors associated with the response to sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: We investigated the prognostic clinicopathologic factors associated with overall survival (os) and progression-free survival (pfs) in the once-daily continuous administration of first-line sunitinib in a consecutive cohort of Turkish patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (rcc).
Methods: The study enrolled 77 Turkish patients with metastatic rcc who received sunitinib in a continuous once-daily dosing regimen between April 2006 and April 2011. Univariate analyses were performed using the log-rank test.
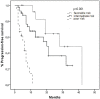
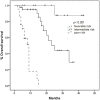
Results: Median follow-up was 18.5 months. In univariate analyses, poor pfs and os were associated with 4 of the 5 factors in the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (mskcc) score: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 2 or higher, low hemoglobin, high corrected serum calcium, and high lactate dehydrogenase. In addition to those factors, hypoalbuminemia, more than 2 metastatic sites, liver metastasis, non-clear cell histology, and the presence of sarcomatoid features on pathology were also associated with poor pfs; and male sex, hypoalbuminemia, prior radiotherapy, more than 2 metastatic sites, lung metastasis, nuclear grade of 3 or 4 for the primary tumour, and the presence of sarcomatoid features were also associated with poorer os. The application of the mskcc model distinctly separated the pfs and os curves (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our study identified prognostic factors for pfs and os with the use sunitinib as first-line metastatic rcc therapy and confirmed that the mskcc model still appears to be valid for predicting survival in metastatic rcc in the era of molecular targeted therapy.
Keywords: Metastatic renal cell carcinoma; first-line therapy; prognostic factors; sarcomatoid features; vascular endothelial growth factor; vegf antagonist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of post-treatment hypoalbuminemia and survival in Chinese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Chin J Cancer. 2017 May 18;36(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0214-7. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28521783 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical efficacy and prognostic factors for overall survival in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with sunitinib.BJU Int. 2012 May;109(9):1349-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10534.x. Epub 2011 Aug 25. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 21883864
-
Prognostic factors for progression-free and overall survival with sunitinib targeted therapy and with cytokine as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Ann Oncol. 2011 Feb;22(2):295-300. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq342. Epub 2010 Jul 25. Ann Oncol. 2011. PMID: 20657034
-
Systematic Review of the Role of Cytoreductive Nephrectomy in the Targeted Therapy Era and Beyond: An Individualized Approach to Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2019 Jan;75(1):111-128. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.09.016. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Eur Urol. 2019. PMID: 30467042
-
The Challenges of Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to the Spine: A Systematic Review of Survival and Treatment.Global Spine J. 2018 Aug;8(5):517-526. doi: 10.1177/2192568217737777. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Global Spine J. 2018. PMID: 30258759 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of serum albumin in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2014 Mar;31(3):841. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0841-7. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24477648
-
Early primary renal tumor response predicts clinical outcome in patients with primary unresectable renal cell carcinoma with synchronous distant metastasis receiving molecularly targeted therapies.Mol Clin Oncol. 2017 Aug;7(2):205-210. doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1294. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28781786 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-lymphocyte Ratio in Place of Neutrophil Count and Platelet Count Improves Prognostic Accuracy of the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium Model.Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jan;50(1):103-110. doi: 10.4143/crt.2017.033. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 28253564 Free PMC article.
-
The association of platelet count with clinicopathological significance and prognosis in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2015 May 8;10(5):e0125538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125538. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25955026 Free PMC article.
-
Association of post-treatment hypoalbuminemia and survival in Chinese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Chin J Cancer. 2017 May 18;36(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0214-7. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28521783 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, et al. In vivo antitumour activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:327–37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

