Simultaneous inhibition of cell-cycle, proliferation, survival, metastatic pathways and induction of apoptosis in breast cancer cells by a phytochemical super-cocktail: genes that underpin its mode of action
- PMID: 24312140
- PMCID: PMC3842439
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.7235
Simultaneous inhibition of cell-cycle, proliferation, survival, metastatic pathways and induction of apoptosis in breast cancer cells by a phytochemical super-cocktail: genes that underpin its mode of action
Abstract
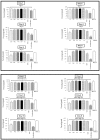
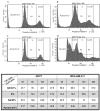
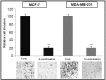
Traditional chemotherapy and radiotherapy for cancer treatment face serious challenges such as drug resistance and toxic side effects. Complementary / Alternative medicine is increasingly being practiced worldwide due to its safety beneficial therapeutic effects. We hypothesized that a super combination (SC) of known phytochemicals used at bioavailable levels could induce 100% killing of breast cancer (BC) cells without toxic effects on normal cells and that microarray analysis would identify potential genes for targeted therapy of BC. Mesenchymal Stems cells (MSC, control) and two BC cell lines were treated with six well established pro-apoptotic phytochemicals individually and in combination (super cocktail), at bioavailable levels. The compounds were ineffective individually. In combination, they significantly suppressed BC cell proliferation (>80%), inhibited migration and invasion, caused cell cycle arrest and induced apoptosis resulting in 100% cell death. However, there were no deleterious effects on MSC cells used as control. Furthermore, the SC down-regulated the expression of PCNA, Rb, CDK4, BcL-2, SVV, and CD44 (metastasis inducing stem cell factor) in the BC cell lines. Microarray analysis revealed several differentially expressed key genes (PCNA, Rb, CDK4, Bcl-2, SVV, P53 and CD44) underpinning SC-promoted BC cell death and motility. Four unique genes were highly up-regulated (ARC, GADD45B, MYLIP and CDKN1C). This investigation indicates the potential for development of a highly effective phytochemical combination for breast cancer chemoprevention / chemotherapy. The novel over-expressed genes hold the potential for development as markers to follow efficacy of therapy.
Keywords: Breast cancer; chemoprevention; metastasis; microarray; phytochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS:
All other authors declare that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Kawasaki BT, Hurt EM, Mistree T, Farrar WL. Targeting cancer stem cells with phytochemicals. Mol Interv. 2008;8:174–84. - PubMed
-
- Gullett NP, Ruhul Amin AR, Bayraktar S. et al. Cancer prevention with natural compounds. Semin Oncol. 2010;37:258–81. - PubMed
-
- Moiseeva EP, Manson MM. Dietary chemopreventive phytochemicals: Too little or too much? Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2009;2:611–6. - PubMed
-
- Mehta RG, Murillo G, Naithani R, Peng X. Cancer chemoprevention by natural products: How far have we come? Pharm Res. 2010;27:950–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

