Molecular Targeted Drugs and Biomarkers in NSCLC, the Evolving Role of Individualized Therapy
- PMID: 24312144
- PMCID: PMC3842443
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.7734
Molecular Targeted Drugs and Biomarkers in NSCLC, the Evolving Role of Individualized Therapy
Abstract
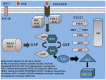
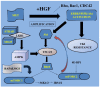
Lung cancer first line treatment has been directed from the non-specific cytotoxic doublet chemotherapy to the molecular targeted. The major limitation of the targeted therapies still remains the small number of patients positive to gene mutations. Furthermore, the differentiation between second line and maintenance therapy has not been fully clarified and differs in the clinical practice between cancer centers. The authors present a segregation between maintenance treatment and second line and present a possible definition for the term "maintenance" treatment. In addition, cancer cell evolution induces mutations and therefore either targeted therapies or non-specific chemotherapy drugs in many patients become ineffective. In the present work pathways such as epidermal growth factor, anaplastic lymphoma kinase, met proto-oncogene and PI3K are extensively presented and correlated with current chemotherapy treatment. Future, perspectives for targeted treatment are presented based on the current publications and ongoing clinical trials.
Keywords: NSCLC; maintenance; pathways; targeted treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Fuster LM, Sandler AB. Select clinical trials of erlotinib (OSI-774) in non-small-cell lung cancer with emphasis on phase III outcomes. Clin Lung Cancer. 2004;6(Suppl 1):S24–9. - PubMed
-
- Alberg AJ, Brock MV, Samet JM. Epidemiology of lung cancer: looking to the future. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3175–85. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.10.462. - PubMed
-
- Vineis P, Airoldi L, Veglia F, Olgiati L, Pastorelli R, Autrup H. et al. Environmental tobacco smoke and risk of respiratory cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in former smokers and never smokers in the EPIC prospective study. BMJ. 2005;330:277.. doi:10.1136/bmj.38327.648472.82. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

