Quantitative statistical methods for image quality assessment
- PMID: 24312148
- PMCID: PMC3840409
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.6815
Quantitative statistical methods for image quality assessment
Abstract
Quantitative measures of image quality and reliability are critical for both qualitative interpretation and quantitative analysis of medical images. While, in theory, it is possible to analyze reconstructed images by means of Monte Carlo simulations using a large number of noise realizations, the associated computational burden makes this approach impractical. Additionally, this approach is less meaningful in clinical scenarios, where multiple noise realizations are generally unavailable. The practical alternative is to compute closed-form analytical expressions for image quality measures. The objective of this paper is to review statistical analysis techniques that enable us to compute two key metrics: resolution (determined from the local impulse response) and covariance. The underlying methods include fixed-point approaches, which compute these metrics at a fixed point (the unique and stable solution) independent of the iterative algorithm employed, and iteration-based approaches, which yield results that are dependent on the algorithm, initialization, and number of iterations. We also explore extensions of some of these methods to a range of special contexts, including dynamic and motion-compensated image reconstruction. While most of the discussed techniques were developed for emission tomography, the general methods are extensible to other imaging modalities as well. In addition to enabling image characterization, these analysis techniques allow us to control and enhance imaging system performance. We review practical applications where performance improvement is achieved by applying these ideas to the contexts of both hardware (optimizing scanner design) and image reconstruction (designing regularization functions that produce uniform resolution or maximize task-specific figures of merit).
Keywords: image quality metrics; local impulse response; resolution; tomography; variance..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

 , as a function of the image
, as a function of the image  . The reconstruction routine seeks to determine the unknown image as some explicit or implicit function,
. The reconstruction routine seeks to determine the unknown image as some explicit or implicit function,  , of the data. For iterative reconstruction, this function is an implicit function given by the maximum of some objective function:
, of the data. For iterative reconstruction, this function is an implicit function given by the maximum of some objective function:  . The objective function,
. The objective function,  , depends on both the goodness of fit between the predicted and measured data and on prior information about the unknown image. At the end of each iteration, the current image
, depends on both the goodness of fit between the predicted and measured data and on prior information about the unknown image. At the end of each iteration, the current image  is replaced by an updated estimate
is replaced by an updated estimate  until some stopping criterion is reached.
until some stopping criterion is reached.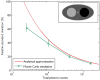


References
-
- Leahy RM, Qi J. Statistical approaches in quantitative positron emission tomography. Stat Comput. 2000;10:147–65.
-
- Shepp LA, Logan BF. The Fourier reconstruction of a head section. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1974;21:21–43.
-
- Barrett HH, Swindell W. Radiological imaging: the theory of image formation, detection, and processing. Academic Press. 1996.
-
- Wilson DW, Tsui BMW. Noise properties of filtered-backprojection and ML-EM reconstructed emission tomographic images. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1993;40:1198–203.
-
- Kaufman L. Implementing and accelerating the EM algorithm for positron emission tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1987;6:37–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

