KSHV LANA and EBV LMP1 induce the expression of UCH-L1 following viral transformation
- PMID: 24314660
- PMCID: PMC4157526
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.10.018
KSHV LANA and EBV LMP1 induce the expression of UCH-L1 following viral transformation
Abstract
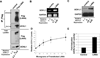
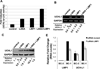
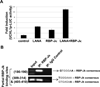
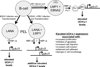
Ubiquitin C-terminal Hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) has oncogenic properties and is highly expressed during malignancies. We recently documented that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection induces uch-l1 expression. Here we show that Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection induced UCH-L1 expression, via cooperation of KSHV Latency-Associated Nuclear Antigen (LANA) and RBP-Jκ and activation of the uch-l1 promoter. UCH-L1 expression was also increased in Primary Effusion Lymphoma (PEL) cells co-infected with KSHV and EBV compared with PEL cells infected only with KSHV, suggesting EBV augments the effect of LANA on uch-l1. EBV latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is one of the few EBV products expressed in PEL cells. Results showed that LMP1 was sufficient to induce uch-l1 expression, and co-expression of LMP1 and LANA had an additive effect on uch-l1 expression. These results indicate that viral latency products of both human γ-herpesviruses contribute to uch-l1 expression, which may contribute to the progression of lymphoid malignancies.
Keywords: EBV; KSHV; LANA; LMP1; UCH-L1.
© 2013 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Basseres E, Coppotelli G, Pfirrmann T, Andersen JB, Masucci M, Frisan T. The ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase UCH-L1 promotes bacterial invasion by altering the dynamics of the actin cytoskeleton. Cellular microbiology. 2010;12:1622–1633. - PubMed
-
- Betarbet R, Sherer TB, Greenamyre JT. Ubiquitin-proteasome system and Parkinson's diseases. Experimental neurology. 2005;191(Suppl 1):S17–S27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

