Pomegranate juice exacerbates oxidative stress and nigrostriatal degeneration in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 24315037
- PMCID: PMC3946191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.10.077
Pomegranate juice exacerbates oxidative stress and nigrostriatal degeneration in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
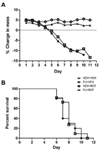
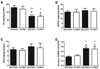
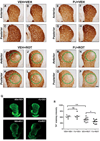
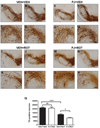
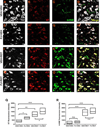
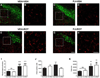
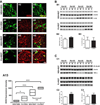
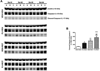
Numerous factors contribute to the death of substantia nigra (SN) dopamine (DA) neurons in Parkinson's disease (PD). Compelling evidence implicates mitochondrial deficiency, oxidative stress, and inflammation as important pathogenic factors in PD. Chronic exposure of rats to rotenone causes a PD-like syndrome, in part by causing oxidative damage and inflammation in substantia nigra. Pomegranate juice (PJ) has the greatest composite antioxidant potency index among beverages, and it has been demonstrated to have protective effects in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease. The present study was designed to examine the potential neuroprotective effects of PJ in the rotenone model of PD. Oral administration of PJ did not mitigate or prevent experimental PD but instead increased nigrostriatal terminal depletion, DA neuron loss, the inflammatory response, and caspase activation, thereby heightening neurodegeneration. The mechanisms underlying this effect are uncertain, but the finding that PJ per se enhanced nitrotyrosine, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and activated caspase-3 expression in nigral DA neurons is consistent with its potential pro-oxidant activity.
Keywords: Inflammation; Mitochondria; Neuroprotection; Neurotoxicity; Oxidative stress; Parkinson's disease; Polyphenols; Pomegranate juice; Rotenone.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no actual or potential conflicts of interest, including any financial, personal or other relationships with people or organizations during the development of the work submitted.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Thymol, a Dietary Monoterpene Against Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Rotenone-Induced Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 27;20(7):1538. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071538. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30934738 Free PMC article.
-
Lycopodium Attenuates Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.Molecules. 2019 Jun 10;24(11):2182. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112182. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31185705 Free PMC article.
-
Phenothiazine normalizes the NADH/NAD+ ratio, maintains mitochondrial integrity and protects the nigrostriatal dopamine system in a chronic rotenone model of Parkinson's disease.Redox Biol. 2019 Jun;24:101164. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101164. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30925294 Free PMC article.
-
Reprint of: revisiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease-resemblance to the effect of amphetamine drugs of abuse.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Sep;62:186-201. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.042. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23743292 Review.
-
Mitochondrial complex I inhibitor rotenone-induced toxicity and its potential mechanisms in Parkinson's disease models.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2012 Aug;42(7):613-32. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2012.680431. Epub 2012 May 11. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22574684 Review.
Cited by
-
An in silico investigation on the inhibitory potential of the constituents of Pomegranate juice on antioxidant defense mechanism: Relevance to neurodegenerative diseases.IBRO Rep. 2019 May 9;6:153-159. doi: 10.1016/j.ibror.2019.05.003. eCollection 2019 Jun. IBRO Rep. 2019. PMID: 31193374 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective role of chrysin in attenuating loss of dopaminergic neurons and improving motor, learning and memory functions in rats.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018 May-Jun;12(3):35-43. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018. PMID: 29896070 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors and nitric oxide in dopaminergic neurotoxicity.World J Psychiatry. 2021 Oct 19;11(10):830-840. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i10.830. eCollection 2021 Oct 19. World J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34733645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioral, neurochemical, and pathologic alterations in bacterial artificial chromosome transgenic G2019S leucine-rich repeated kinase 2 rats.Neurobiol Aging. 2015 Jan;36(1):505-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.07.011. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Neurobiol Aging. 2015. PMID: 25174649 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic alpha-synuclein fibrils cause mitochondrial impairment and selective dopamine neurodegeneration in part via iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Aug;74(15):2851-2874. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2541-x. Epub 2017 May 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28534083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abercrombie ED, et al. Effects of L-dopa on extracellular dopamine in striatum of normal and 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats. Brain Res. 1990;525:36–44. - PubMed
-
- Aviram M, et al. Pomegranate phenolics from the peels, arils, and flowers are antiatherogenic: studies in vivo in atherosclerotic apolipoprotein e-deficient (E 0) mice and in vitro in cultured macrophages and lipoproteins. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:1148–1157. - PubMed
-
- Babich H, et al. Glutathione as a mediator of the in vitro cytotoxicity of a green tea polyphenol extract. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2007;17:357–369. - PubMed
-
- Bashkatova V, et al. Chronic administration of rotenone increases levels of nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation products in rat brain. Exp Neurol. 2004;186:235–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

