Intracellular complement activation sustains T cell homeostasis and mediates effector differentiation
- PMID: 24315997
- PMCID: PMC3865363
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.018
Intracellular complement activation sustains T cell homeostasis and mediates effector differentiation
Abstract
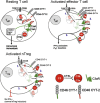
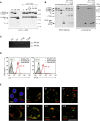
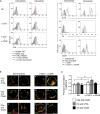
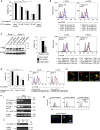
Complement is viewed as a critical serum-operative component of innate immunity, with processing of its key component, C3, into activation fragments C3a and C3b confined to the extracellular space. We report here that C3 activation also occurred intracellularly. We found that the T cell-expressed protease cathepsin L (CTSL) processed C3 into biologically active C3a and C3b. Resting T cells contained stores of endosomal and lysosomal C3 and CTSL and substantial amounts of CTSL-generated C3a. While "tonic" intracellular C3a generation was required for homeostatic T cell survival, shuttling of this intracellular C3-activation-system to the cell surface upon T cell stimulation induced autocrine proinflammatory cytokine production. Furthermore, T cells from patients with autoimmune arthritis demonstrated hyperactive intracellular complement activation and interferon-γ production and CTSL inhibition corrected this deregulated phenotype. Importantly, intracellular C3a was observed in all examined cell populations, suggesting that intracellular complement activation might be of broad physiological significance.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
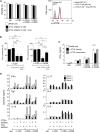
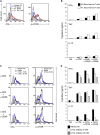
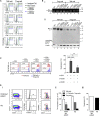
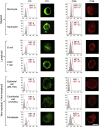
Comment in
-
New twist on an ancient innate immune pathway.Immunity. 2013 Dec 12;39(6):1000-2. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.015. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 24332028 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity: The inside story on complement activation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Feb;14(2):61. doi: 10.1038/nri3603. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24378841 No abstract available.
References
-
- André C., Cota D. Coupling nutrient sensing to metabolic homoeostasis: the role of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 pathway. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2012;71:502–510. - PubMed
-
- Chen G., Shaw M.H., Kim Y.-G., Nuñez G. NOD-like receptors: role in innate immunity and inflammatory disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009;4:365–398. - PubMed
-
- Couzi L., Contin-Bordes C., Marliot F., Sarrat A., Grimal P., Moreau J.-F., Merville P., Fremeaux-Bacchi V. Inherited deficiency of membrane cofactor protein expression and varying manifestations of recurrent atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in a sibling pair. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008;52:e5–e9. - PubMed
-
- Dehrmann F.M., Coetzer T.H., Pike R.N., Dennison C. Mature cathepsin L is substantially active in the ionic milieu of the extracellular medium. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995;324:93–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

